Accuracy of Nasal Nitric Oxide Measurement as a Diagnostic Test for Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 28481653
- PMCID: PMC6137897
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201701-062SR
Accuracy of Nasal Nitric Oxide Measurement as a Diagnostic Test for Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Rationale: Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) is a rare disorder causing chronic otosinopulmonary disease, generally diagnosed through evaluation of respiratory ciliary ultrastructure and/or genetic testing. Nasal nitric oxide (nNO) measurement is used as a PCD screening test because patients with PCD have low nNO levels, but its value as a diagnostic test remains unknown.
Objectives: To perform a systematic review to assess the utility of nNO measurement (index test) as a diagnostic tool compared with the reference standard of electron microscopy (EM) evaluation of ciliary defects and/or detection of biallelic mutations in PCD genes.
Data sources: Ten databases were searched for reference sources from database inception through July 29, 2016.
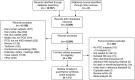
Data extraction: Study inclusion was limited to publications with rigorous nNO index testing, reference standard diagnostic testing with EM and/or genetics, and calculable diagnostic accuracy information for cooperative patients (generally >5 yr old) with high suspicion of PCD.
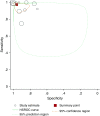
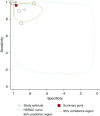
Synthesis: Meta-analysis provided a summary estimate for sensitivity and specificity and a hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic curve. The Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 tool was used to assess study quality, and Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation was used to assess the certainty of evidence. In 12 study populations (1,344 patients comprising 514 with PCD and 830 without PCD), using a reference standard of EM alone or EM and/or genetic testing, summary sensitivity was 97.6% (92.7-99.2) and specificity was 96.0% (87.9-98.7), with a positive likelihood ratio of 24.3 (7.6-76.9), a negative likelihood ratio of 0.03 (0.01-0.08), and a diagnostic odds ratio of 956.8 (141.2-6481.5) for nNO measurements. After studies using EM alone as the reference standard were excluded, the seven studies using an extended reference standard of EM and/or genetic testing showed a summary sensitivity of nNO measurements of 96.3% (88.7-98.9) and specificity of 96.4% (85.1-99.2), with a positive likelihood ratio of 26.5 (5.9-119.1), a negative likelihood ratio of 0.04 (0.01-0.12), and a diagnostic odds ratio of 699.3 (67.4-7256.0). Certainty of the evidence was graded as moderate.
Conclusions: nNO is a sensitive and specific test for PCD in cooperative patients (generally >5 yr old) with high clinical suspicion for this disease. With a moderate level of evidence, this meta-analysis confirms that nNO testing using velum closure maneuvers has diagnostic accuracy similar to EM and/or genetic testing for PCD when cystic fibrosis is ruled out. Thus, low nNO values accompanied by an appropriate clinical phenotype could be used as a diagnostic PCD test, though EM and/or genetics will continue to provide confirmatory information.
Keywords: Kartagener syndrome; nitric oxide; primary ciliary dyskinesia.
Figures



References
-
- Kempeneers C, Seaton C, Chilvers MA. Variation of ciliary beat pattern in three different beating planes in healthy subjects. Chest. 2017;151:993–1001. - PubMed
-
- Zariwala MA, Knowles MR, Leigh MW. Primary ciliary dyskinesia. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJH, Bird TD, Ledbetter N, Mefford HC, Smith RJH, et al., editors. GeneReviews. Seattle, WA: University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2017 [2007 Jan 24; updated 2015 Sep 3] - PubMed
-
- Collins SA, Behan L, Harris A, Gove K, Lucas JS. The dangers of widespread nitric oxide screening for primary ciliary dyskinesia. Thorax. 2016;71:560–561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

