Contextual influences affecting patterns of overweight and obesity among university students: a 50 universities population-based study in China
- PMID: 28482842
- PMCID: PMC5423012
- DOI: 10.1186/s12942-017-0092-x
Contextual influences affecting patterns of overweight and obesity among university students: a 50 universities population-based study in China
Abstract
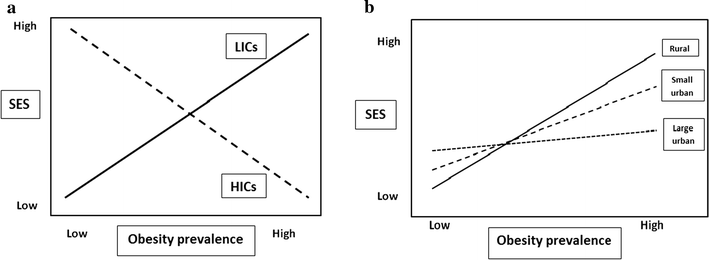
Background: Many studies have examined childhood and adolescent obesity, but few have examined young adults and the effect of their home and current living environments on prevalence rates. The present study explores contextual factors affecting overweight and obesity among university students in China and, in particular, focuses on how the SES-obesity relationship varies across different geographical contexts.
Methods: Participants were 11,673 students, who were identified through a multistage survey sampling process conducted in 50 universities. Individual data was obtained through a self-administered questionnaire, and contextual variables were retrieved from a national database. Multilevel logistic regression models were used to examine urban and regional variations in overweight and obesity.
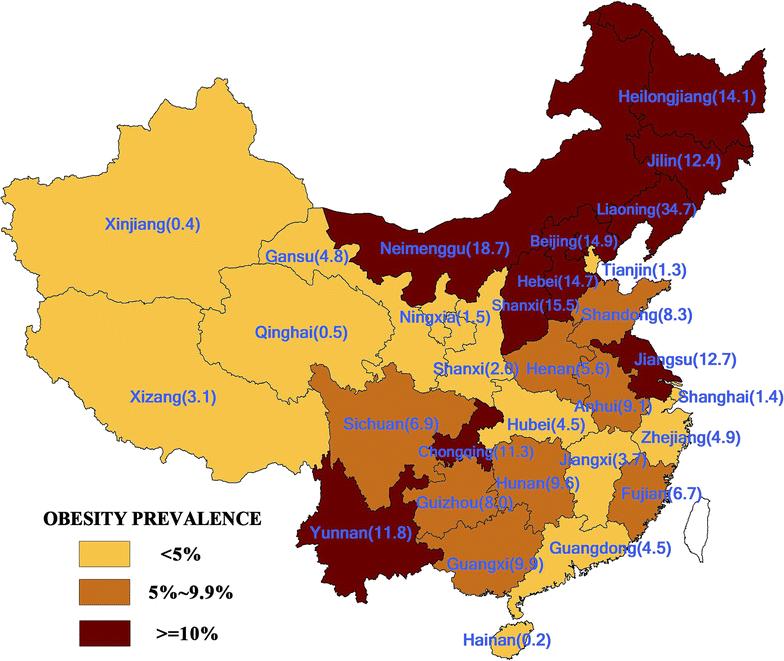
Results: Overall the prevalence of overweight and obesity in the study sample was 9.5% (95% CI 7.7, 11.3%). After controlling for individual factors, both attributes of the home location (regional GDP <gross domestic product> per capita and rurality) and the current university location (city population) were found to be important, thus suggesting that the different origins of students affect current levels of obesity. At the individual level, while students with more financial resources were more likely to be obese, the extent of this relationship was highly dependent upon area income and city size.
Conclusion: The results of this study add important insights about the role of contextual factors affecting overweight and obesity among young adults and indicate a need to take into account both past as well as present environmental influences when considering the role of contextual factors in models of the nutrition transition.
Keywords: China; Context effects; Overweight and obesity; Young adults.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overweight and Obesity Among Chinese College Students: An Exploration of Gender as Related to External Environmental Influences.Am J Mens Health. 2018 Jul;12(4):926-934. doi: 10.1177/1557988317750990. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Am J Mens Health. 2018. PMID: 29325480 Free PMC article.
-
Regional contextual influences on short sleep duration: a 50 universities population-based multilevel study in China.Glob Health Action. 2018;11(1):1442684. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2018.1442684. Glob Health Action. 2018. PMID: 29495949 Free PMC article.
-
Regional contextual determinants of internet addiction among college students: a representative nationwide study of China.Eur J Public Health. 2017 Dec 1;27(6):1032-1037. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckx141. Eur J Public Health. 2017. PMID: 29077834
-
Individual and regional factors affecting stress and problem alcohol use: A representative nationwide study of China.Health Place. 2018 May;51:19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2018.02.008. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Health Place. 2018. PMID: 29518714
-
WebWise: guide to the Washington University Center for Genetics in Medicine web site.Genome Res. 1998 Jul;8(7):686-9. doi: 10.1101/gr.8.7.686. Genome Res. 1998. PMID: 9685315 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Investigating the Interrelationships Between Obesity, Academic Achievement, Physical Activity, and Social Support Among Jazan University Students.Mater Sociomed. 2024;36(1):59-64. doi: 10.5455/msm.2024.36.59-64. Mater Sociomed. 2024. PMID: 38590594 Free PMC article.
-
Urban Scaling of Health Outcomes: a Scoping Review.J Urban Health. 2022 Jun;99(3):409-426. doi: 10.1007/s11524-021-00577-4. Epub 2022 May 5. J Urban Health. 2022. PMID: 35513600 Free PMC article.
-
Overweight and Obesity Among Chinese College Students: An Exploration of Gender as Related to External Environmental Influences.Am J Mens Health. 2018 Jul;12(4):926-934. doi: 10.1177/1557988317750990. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Am J Mens Health. 2018. PMID: 29325480 Free PMC article.
-
Scaling of cardiovascular risk factors in 230 Latin American cities.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 1;15(1):7279. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92087-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40025192 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the impact of physical factors on the overweight and obese physical therapy students.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2020 Oct 23;15(6):479-485. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2020.09.004. eCollection 2020 Dec. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33318739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, Mullany EC. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384:766–781. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pearce J, Witten K, editors. Geographies of obesity: environmental understandings of the obesity epidemic. Burlinton: Ashgate Publishing Ltd; 2010.
-
- Kim D, Kawachi I. Contextual determinants of obesity: an overview. In: Pearce J, Witten K, editors. Geographies of obesity: environmental understandings of the obesity epidemic. Burlinton: Ashgate Publishing Ltd; 2010. pp. 39–54.
-
- Popkin BM. The nutrition transition and obesity in the developing world. J Nutr. 2001;131:871S–873S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

