Therapeutic effect of Schistosoma japonicum cystatin on bacterial sepsis in mice
- PMID: 28482922
- PMCID: PMC5422996
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-017-2162-0
Therapeutic effect of Schistosoma japonicum cystatin on bacterial sepsis in mice
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is a life-threatening complication of an infection and remains one of the leading causes of mortality in surgical patients. Bacteremia induces excessive inflammatory responses that result in multiple organ damage. Chronic helminth infection and helminth-derived materials have been found to immunomodulate host immune system to reduce inflammation against some allergic or inflammatory diseases. Schistosoma japonicum cystatin (Sj-Cys) is a cysteine protease inhibitor that induces regulatory T-cells and a potential immunomodulatory. The effect of Sj-Cys on reducing sepsis inflammation and mortality was investigated.
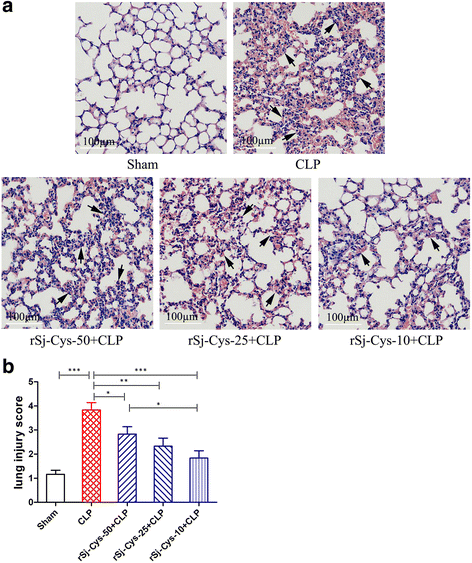
Methods: Sepsis was induced in BALB/c mice using cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), followed by intraperitoneal injection of different doses (10, 25 or 50 μg) of recombinant Sj-Cys (rSj-Cys). The therapeutic effect of rSj-Cys on sepsis was evaluated by observing the survival rates of mice for 96 h after CLP and the pathological injury of liver, kidney and lung by measuring the levels of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine (Cr) in sera and the tissue sections pathology, and the expression of MyD88 in liver, kidney and lung tissues. The immunological mechanism was investigated by examining pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β) and IL-10 and TGF-β1 in mice sera and in culture of macrophages stimulated by lipopolysaccharides (LPS).
Results: rSj-Cys treatment provided significant therapeutic effects on CLP-induced sepsis in mice demonstrated with increased survival rates, alleviated overall disease severity and tissue injury of liver, kidney and lung. The rSj-Cys conferred therapeutic efficacy was associated with upregualted IL-10 and TGF-β1 cytokines and reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β. MyD88 expression in liver, kidney and lung tissues of rSj-Cys-treated mice was reduced. In vitro assay with macrophages also showed that rSj-Cys inhibited the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediator nitric oxide (NO) after being stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Conclusions: The results suggest the anti-inflammatory potential of rSj-Cys as a promising therapeutic agent on sepsis. The immunological mechanism underlying its therapeutic effect may involve the downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulation of IL-10 and TGF-β1 cytokines possibly via downregulation of the TLR adaptor-transducer MyD88 pathway. The findings suggest rSj-Cys is a potential therapeutic agent for sepsis and other inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Cecal ligation and puncture; Cystatin; Immunomodulation; Schistosoma japonicum; Sepsis.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Therapeutic efficacy of Schistosoma japonicum cystatin on sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy in a mouse model.Parasit Vectors. 2020 May 18;13(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04104-3. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32423469 Free PMC article.
-
Trichinella spiralis cystatin alleviates polymicrobial sepsis through activating regulatory macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Aug;109:108907. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108907. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35691271
-
Schistosoma japonicum cystatin attenuated CLP-induced sepsis in mice though inducing tolerogenic dendritic cells and regulatory T cells.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025 Jun;120:102345. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2025.102345. Epub 2025 May 7. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40344985
-
A Potential Therapeutic Target RNA-binding Protein, Arid5a for the Treatment of Inflammatory Disease Associated with Aberrant Cytokine Expression.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(16):1766-1771. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180426103753. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 29701145 Review.
-
Ameliorating effects of berberine on sepsis-associated lung inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide: molecular mechanisms and preclinical evidence.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Aug;75(4):805-816. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00492-2. Epub 2023 May 15. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37184743 Review.
Cited by
-
Schistosoma japonicum Cystatin Alleviates Sepsis Through Activating Regulatory Macrophages.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 24;11:617461. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.617461. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33718268 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Effect of Schistosoma japonicum Cystatin on Atherosclerotic Renal Damage.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 25;9:760980. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.760980. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34901005 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory proteins from hookworms reduce cardiac inflammation and modulate regulatory responses in a mouse model of chronic Trypanosoma cruzi infection.Front Parasitol. 2023;2:1244604. doi: 10.3389/fpara.2023.1244604. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Front Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 38239430 Free PMC article.
-
Micromotor-Enabled Active Hydrogen and Tobramycin Delivery for Synergistic Sepsis Therapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Nov;10(33):e2303759. doi: 10.1002/advs.202303759. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37818787 Free PMC article.
-
Schistosoma japonicum cystatin has protective effects against "two-hit" sepsis in mice by regulating the inflammatory microenvironment.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Jan 20;45(1):110-117. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.14. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 39819719 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
References
-
- Huang L, Wang C, Naren G, Aori G. Effect of geniposide on LPS-induced activation of TLR4-NF-kappaB pathway in RAW264.7 macrophage cell line. Chin J Cell Mol Imm. 2013;29:1012–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

