Metabolic Radiomics for Pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT to Characterize Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Histopathologic Characteristics, Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, and Prognosis
- PMID: 28484211
- PMCID: PMC5431555
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01524-7
Metabolic Radiomics for Pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT to Characterize Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Histopathologic Characteristics, Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, and Prognosis
Abstract
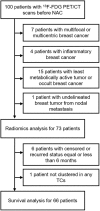
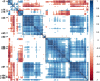
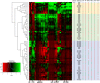
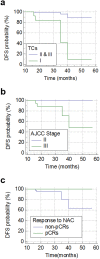
Radiomics has been spotlighted as imaging biomarker for estimation of intratumoral heterogeneity (ITH) which is regarded as the main reason for resistance to tumor treatment. Although a number of studies has shown clinical evidences that separate measurement of metabolic ITH by texture features (TFs) on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) has prognostic ability in various tumors, there has been no consensus regarding the best parameter representing ITH. Besides, it is yet uncertain that TFs are useful for estimation of histopathologic markers, prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC), or prognostic ability in breast cancer. To depart from the traditional approach, we evaluated the clinical usefulness of integrated metabolic radiomics using unsupervised clustering with 109 TFs measured from pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT scans of 73 patients with locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) underwent NAC before surgery. Our study shows that metabolic radiomics patterns of LABC are associated with Ki67 expression, achievement of pathologic complete response after NAC, and risk of recurrence. Integrated metabolic radiomics has potential for clinically relevant pretreatment biomarker with predictive and prognostic ability for personalized management in LABC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predicting neo-adjuvant chemotherapy response and progression-free survival of locally advanced breast cancer using textural features of intratumoral heterogeneity on F-18 FDG PET/CT and diffusion-weighted MR imaging.Breast J. 2019 May;25(3):373-380. doi: 10.1111/tbj.13032. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Breast J. 2019. PMID: 29602210
-
Complete Metabolic Response on Interim 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography to Predict Long-Term Survival in Patients with Breast Cancer Undergoing Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy.Oncologist. 2017 May;22(5):526-534. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0334. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28377466 Free PMC article.
-
The Value of 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging Combined With Pretherapeutic Ki67 for Early Prediction of Pathologic Response After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Feb;95(8):e2914. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002914. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 26937935 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of 18F-FDG PET and PET/CT for assessment of treatment response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 31;22(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01350-2. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33129348 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of SUVmax measuring on primary lesion and ALN by 18F-FDG PET or PET/CT in patients with breast cancer.Eur J Radiol. 2018 Aug;105:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.05.014. Epub 2018 May 17. Eur J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30017264 Review.
Cited by
-
PET/CT-based radiomics analysis may help to predict neoadjuvant chemotherapy outcomes in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 7;12:849626. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.849626. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36419895 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Machine Learning Analyses Using Clinical and [18F]-FDG-PET/CT Radiomic Characteristics to Predict Recurrence in Patients with Breast Cancer.Mol Imaging Biol. 2023 Oct;25(5):923-934. doi: 10.1007/s11307-023-01823-8. Epub 2023 May 16. Mol Imaging Biol. 2023. PMID: 37193804
-
Progress and Future Trends in PET/CT and PET/MRI Molecular Imaging Approaches for Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 12;10:1301. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01301. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32903496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Applications of Radiomics in Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Oncology: Opportunities and Challenges.Theranostics. 2019 Feb 12;9(5):1303-1322. doi: 10.7150/thno.30309. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 30867832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Value of PET.CT Based on Big Data in Colorectal and Peritoneal Metastatic Cancer.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Sep 30;2022:6120337. doi: 10.1155/2022/6120337. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. Retraction in: Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9795808. doi: 10.1155/2023/9795808. PMID: 36262991 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Yoon H-J, et al. Correlation of breast cancer subtypes, based on estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2, with functional imaging parameters from 68Ga-RGD PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2014;41:1534–1543. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2744-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Groheux, D. et al. Early Metabolic Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment: FDG PET/CT Criteria according to Breast Cancer Subtype. Radiology 277, 358–371 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

