Development and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier in the Context of Metabolic Control
- PMID: 28484368
- PMCID: PMC5399017
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00224
Development and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier in the Context of Metabolic Control
Abstract
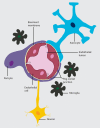
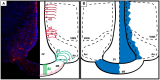
Under physiological conditions, the brain consumes over 20% of the whole body energy supply. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) allows dynamic interactions between blood capillaries and the neuronal network in order to provide an adequate control of molecules that are transported in and out of the brain. Alterations in the BBB structure and function affecting brain accessibility to nutrients and exit of toxins are found in a number of diseases, which in turn may disturb brain function and nutrient signaling. In this review we explore the major advances obtained in the understanding of the BBB development and how its structure impacts on function. Furthermore, we focus on the particularities of the barrier permeability in the hypothalamus, its role in metabolic control and the potential impact of hypothalamic BBB abnormities in metabolic related diseases.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; development; hypothalamus; inflammation; neurovascular unit; obesity.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

