Rapid Identification and Isolation of Inhibitors of Rat Lens Aldose Reductase and Antioxidant in Maackia amurensis
- PMID: 28484711
- PMCID: PMC5397615
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/4941825
Rapid Identification and Isolation of Inhibitors of Rat Lens Aldose Reductase and Antioxidant in Maackia amurensis
Abstract
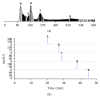
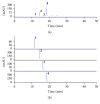
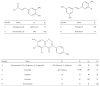
Oxidative stress and aldose reductase activity have been implicated in the development of diabetic complications. In this study, the antioxidant and aldose reductase (AR) inhibitory effects of Maackia amurensis (MA) were investigated. The ethyl acetate fraction of the MA extract showed the highest inhibitory activity in antioxidant and rat lens AR (RLAR). To identify and isolate the active components in the ethyl acetate fraction of the MA extract, high-speed countercurrent chromatography and Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography were performed and guided by an offline HPLC-ABTS assay and HPLC microfractionation AR assay. Four antioxidants, namely, piceatannol (IC50 = 6.73 μM), resveratrol (IC50 = 11.05 μM), trans-ferulic acid (IC50 = 13.51 μM), and chlorogenic acid (IC50 = 27.23 μM), and six AR inhibitors, namely, chlorogenic acid (IC50 = 4.2 μM), tectoridin (IC50 = 50.4 μM), genistein (IC50 = 57.1 μM), formononetin (IC50 = 69.2 μM), resveratrol (IC50 = 117.6 μM), and daidzein (IC50 = 151.9 μM), were isolated and identified. The screening results of the offline HPLC-ABTS assay and HPLC microfractionation AR assay matched the activity of isolated compounds. Thus, MA is potentially valuable for antioxidant and AR inhibitor discovery and efficient drug design for the prevention and treatment of diabetic complications.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

