A Specific and Covalent JNK-1 Ligand Selected from an Encoded Self-Assembling Chemical Library
- PMID: 28485044
- PMCID: PMC5557334
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201701644
A Specific and Covalent JNK-1 Ligand Selected from an Encoded Self-Assembling Chemical Library
Abstract
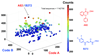
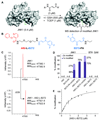
We describe the construction of a DNA-encoded chemical library comprising 148 135 members, generated through the self-assembly of two sub-libraries, containing 265 and 559 members, respectively. The library was designed to contain building blocks potentially capable of forming covalent interactions with target proteins. Selections performed with JNK1, a kinase containing a conserved cysteine residue close to the ATP binding site, revealed the preferential enrichment of a 2-phenoxynicotinic acid moiety (building block A82) and a 4-(3,4-difluorophenyl)-4-oxobut-2-enoic acid moiety (building block B272). When the two compounds were joined by a short PEG linker, the resulting bidentate binder (A82-L-B272) was able to covalently modify JNK1 in the presence of a large molar excess of glutathione (0.5 mm), used to simulate intracellular reducing conditions. By contrast, derivatives of the individual building blocks were not able to covalently modify JNK1 in the same experimental conditions. The A82-L-B272 ligand was selective over related kinases (BTK and GAK), which also contain targetable cysteine residues in the vicinity of the active site.
Keywords: DNA-encoded chemical libraries; covalent inhibitors; drug discovery; kinases; targetable cysteine.
© 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

References
-
- Lerner RA, Brenner S. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2017;56:1664–1165. - PubMed
- Yuen LH, Franzini RM. Chembiochem. 2016 doi: 10.1002/cbic.201600567. - DOI
- Zimmermann G, Neri D. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21:1828–1834. - PMC - PubMed
- Kleiner RE, Dumelin CE, Liu DR. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40:5707–5717. - PMC - PubMed
- Shi B, Zhou Y, Huang Y, Zhang J, Li X. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017;27:361–369. - PubMed
- Zambaldo C, Barluenga S, Winssinger N. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015;26:8–15. - PubMed
- Blakskjaer P, Heitner T, Hansem NJV. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015;26:62–71. - PubMed
- Clark MA, Acharya RA, Arico–Muendel CC, Belyanskaya SL, Benjamin DR, Carlson NR, Centrella PA, Chiu CH, Creaser SP, Cuozzo JW, Davie CP, et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2009;5:647–654. - PubMed
- Petersen LK, Blakskjær P, Chaikuad A, Christensen AB, Dietvorst J, Holmkvist J, Knapp S, Kořínek M, Pedersen AE, Röhm S, Sløk FA, et al. Med Chem Commun. 2016;7:1332–1339.
-
- McCafferty J, Griffiths AD, Winter G, Chiswell DJ. Nature. 1990;348:552–554. - PubMed
- Kang AS, Barbas CF, Janda KD, Benkovic SJ, Lerner RA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:3750–3755.
- Boder ET, Wittrup KD. Nature Biotechnol. 1997;15:553–557. - PubMed
- Wilson DS, Keefe AD, Szostak JW. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:3750–3755. - PMC - PubMed
- Hansen J, Pluckthun A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:4937–4942. - PMC - PubMed
- Ellington AD, Szostak JW. Nature. 1990;346:818–822. - PubMed
- Tuerk C, Gold L. Science. 1990;249:505–510. - PubMed
-
- Wichert M, Krall N, Decurtins W, Franzini RM, Pretto F, Schneider P, Neri D, Scheuermann J. Nat Chem. 2015;7:241–249. - PubMed
-
- Melkko S, Zhang Y, Dumelin CE, Scheuermann J, Neri D. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007;46:4671–4674. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

