A Novel Porcine Model of Septic Shock Induced by Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome due to Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 28485324
- PMCID: PMC5443030
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.205854
A Novel Porcine Model of Septic Shock Induced by Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome due to Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is one of the main causes of mortality in critically ill patients following progression to septic shock. To investigate the pathophysiologic changes of sepsis, we developed a novel porcine model of septic shock induced by acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA) pneumonia.
Methods: Twenty-six male Landraces (Lvyuanweiye, Beijing, China) weighing 30 ± 2 kg were divided into four groups: sham group (SH; n = 5); cotton smoke inhalation group (SM; n = 6); MRSA pneumonia group (MR; n = 6); and septic shock group with cotton smoke inhalation + MRSA pneumonia (SS; n = 9). Extensive hemodynamics, oxygen dynamics, and lung function were monitored for 24 h following the injury or until death. Tissues were collected, and histopathology evaluations were carried out.
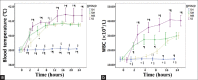
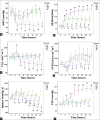
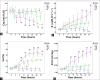
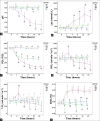
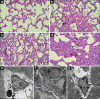
Results: Blood cultures from 6 of 9 animals in the SS group were positive for MRSA. Two hours following the injury, decreased mean arterial blood pressure (60-70 mmHg) and cardiac index (<2 L.min-1.m-2) were observed in the animals in the SS group, while systemic vascular resistance index was increased. The hemodynamic characteristics of septic shock were only observed in the SS group but not significant in the other groups. The PO2/FiO2in the SM and SS groups decreased to 300 and 100, respectively. In the SS group, extravascular lung water index increased to 20 ml/kg, whereas thoracopulmonary compliance decreased to 10 ml/H2O after injury. Deterioration of pulmonary function in the SS group was more serious than the SM and MR groups. Severe lung injury in the SS group was confirmed by the histopathology evaluations. The lung injury confirmed by high-resolution thin-section computed tomography and histopathology in the SS group was more serious than those of other groups.
Conclusions: In the present study, we developed a novel porcine model of septic shock induced by ARDS due to severe MRSA pneumonia with characteristic hyperdynamic and hypodynamic phases in 24 h, which mimicked the hemodynamic changing of septic shock in human.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel ovine model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-induced pneumonia and sepsis.Shock. 2008 May;29(5):642-9. doi: 10.1097/shk.0b013e318158125b. Shock. 2008. PMID: 17885644
-
Chemically modified tetracycline prevents the development of septic shock and acute respiratory distress syndrome in a clinically applicable porcine model.Shock. 2005 Oct;24(4):348-56. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000180619.06317.2c. Shock. 2005. PMID: 16205320
-
Effects of severe smoke inhalation injury and septic shock on global hemodynamics and microvascular blood flow in sheep.Shock. 2006 Nov;26(5):489-95. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000230300.78515.ed. Shock. 2006. PMID: 17047520
-
[Management of septic shock and acquired respiratory distress syndrome in pediatric cancer patients].Klin Padiatr. 2005 Nov;217 Suppl 1:S130-42. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-872507. Klin Padiatr. 2005. PMID: 16288359 Review. German.
-
Community-acquired pneumonia and bacteremia due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying Panton-Valentine-leukocidin gene in Greece: two case reports and literature review.J Chemother. 2007 Dec;19(6):703-8. doi: 10.1179/joc.2007.19.6.703. J Chemother. 2007. PMID: 18230554 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of ulinastatin on renal perfusion evaluated by Doppler ultrasonography in a porcine model of septic shock.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Nov;22(5):1324. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10759. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34630678 Free PMC article.
-
Association of high-resolution computed tomography score with ventilator weaning and 28-day mortality of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome.J Int Med Res. 2020 Jun;48(6):300060520912966. doi: 10.1177/0300060520912966. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32520632 Free PMC article.
-
Temporary bilateral clamping of renal arteries induces ischemia-reperfusion: A new pig model of acute kidney injury using total intravenous anesthesia.Physiol Rep. 2025 Feb;13(3):e70203. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70203. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39895016 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of miR-146b-3p protects septic mice with acute respiratory distress syndrome by inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2020 Aug;52(4):229-236. doi: 10.1007/s10863-020-09839-3. Epub 2020 Jun 2. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 32488541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–54. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022139. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Xu F, Shi LY, Diao R, Cheng YS, Chen XY, et al. Efficacy and significance of various scores for pneumonia severity in the management of patients with community-acquired pneumonia in China. Chin Med J. 2012;125:639–45. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.2012.04.015. - PubMed
-
- Stapleton RD, Wang BM, Hudson LD, Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell ES, Steinberg KP. Causes and timing of death in patients with ARDS. Chest. 2005;128:525–32. doi: 10.1378/chest.128.2.525. - PubMed
-
- Li DZ, Chen YS, Yang JP, Zhang W, Hu CP, Li JS, et al. Preliminary molecular epidemiology of the Staphylococcus aureus in lower respiratory tract infections: A multicenter study in China. Chin Med J. 2011;124:687–92. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.2011.05.010. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

