A pharmacodynamic modelling and simulation study identifying gender differences of daily olanzapine dose and dopamine D2-receptor occupancy
- PMID: 28486094
- PMCID: PMC5557349
- DOI: 10.1080/08039488.2017.1314011
A pharmacodynamic modelling and simulation study identifying gender differences of daily olanzapine dose and dopamine D2-receptor occupancy
Abstract
Background: Gender differences in treatment response rates for patients treated with antipsychotics are known. However, the literature lacks a pharmacodynamic model to allow for gender-based clinical trial simulations from modelling parameters for Olanzapine and dopamine D2 receptor occupancy. Thus, the primary aim of this analysis is to test and quantify the effect of gender on the pharmacodynamics of Olanzapine.
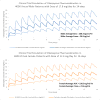
Methods: Population pharmacodynamic modelling was performed using non-linear mixed effects modelling in MONOLIX, while the Clinical Trial Simulations were performed using R for statistical programming. The pharmacometric analysis is based on a pooled data approach from three clinical studies where patients were diagnosed with schizophrenia and one clinical study where the patients were diagnosed with bipolar disorder.
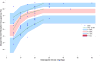
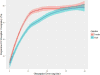
Results: Olanzapine D2RO was modelled using an Emax model in a study population of 70 patients. Population pharmacodynamic parameters were estimated to be: Emax = 85.6% (RSE = 3%), ED50-Men = 5.15 mg/day (RSE = 14) and ED50-Women = 2.38 mg/day (RSE = 34%), with the p-value = 0.037 for the gender-stratified ED50 results.
Conclusion: The pharmacometrics analysis and model-based dosing simulations suggest that, in order to achieve 70% D2RO, women require a 10 mg/day dose and men require approximately a 20 mg/day dose of Olanzapine. Further, clinical implications exist suggesting that clinicians should factor patient gender when considering both a starting dose, as well a, a maintenance dose for patients prescribed Olanzapine due to quantifiable gender-differences of striatal dopamine D2 receptor occupancy.
Keywords: D2RO; Olanzapine; dopamine; gender differences; pharmacodynamics; psychiatry.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Kelly DL, Conley RR, Tamminga CA. Differential olanzapine plasma concentrations by sex in a fixed-dose study. Schizophr Res. 1999;40(2):101–4. - PubMed
-
- Gex-Fabry M, Balant-Gorgia AE, Balant LP. Therapeutic drug monitoring of olanzapine: the combined effect of age, gender, smoking, and comedication. Ther Drug Monit [Internet] 2003;25(1):46–53. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12548144. - PubMed
-
- Usall J, Suarez D, Haro JM, Group SS Gender differences in response to antipsychotic treatment in outpatients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry research. 2007:225–31. Internet. Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med4&NEWS=N&AN=.... - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JM, Cohen LS, Horton NJ, Lee H, Andersen S, Tohen M, et al. Sex differences in clinical response to olanzapine compared with haloperidol. Psychiatry Res. 2002;110(1):27–37. - PubMed
-
- Talonen S, Väänänen J, Kaltiala-Heino R. Gender differences in first onset Schizophrenia spectrum psychoses. Nord J Psychiatry [Internet] 2017 Feb 17;71(2):131–8. cited 2017 Jan 19. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/08039488.2016.1245783. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
