Hippo Signaling Suppresses Cell Ploidy and Tumorigenesis through Skp2
- PMID: 28486106
- PMCID: PMC5863541
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.04.004
Hippo Signaling Suppresses Cell Ploidy and Tumorigenesis through Skp2
Abstract
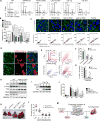
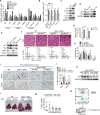
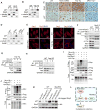
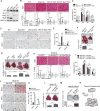
Polyploidy can lead to aneuploidy and tumorigenesis. Here, we report that the Hippo pathway effector Yap promotes the diploid-polyploid conversion and polyploid cell growth through the Akt-Skp2 axis. Yap strongly induces the acetyltransferase p300-mediated acetylation of the E3 ligase Skp2 via Akt signaling. Acetylated Skp2 is exclusively localized to the cytosol, which causes hyper-accumulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27, leading to mitotic arrest and subsequently cell polyploidy. In addition, the pro-apoptotic factors FoxO1/3 are overly degraded by acetylated Skp2, resulting in polyploid cell division, genomic instability, and oncogenesis. Importantly, the depletion or inactivation of Akt or Skp2 abrogated Hippo signal deficiency-induced liver tumorigenesis, indicating their epistatic interaction. Thus, we conclude that Hippo-Yap signaling suppresses cell polyploidy and oncogenesis through Skp2.
Keywords: Hippo; Skp2; Yap; genomic instability; p27; polyploidy; tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Induction of Chromosome Instability by Activation of Yes-Associated Protein and Forkhead Box M1 in Liver Cancer.Gastroenterology. 2017 Jun;152(8):2037-2051.e22. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.018. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28249813
-
Erbin loss promotes cancer cell proliferation through feedback activation of Akt-Skp2-p27 signaling.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Jul 31;463(3):370-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.05.071. Epub 2015 May 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26025650
-
Early mitotic inhibitor-1, an anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome inhibitor, can control tumor cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with Skp2 stability and degradation of p27(Kip1).Hum Pathol. 2013 Mar;44(3):365-73. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2012.03.030. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Hum Pathol. 2013. PMID: 22995332
-
Role of the transcriptional coactivators YAP/TAZ in liver cancer.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019 Dec;61:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2019.07.006. Epub 2019 Aug 3. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31387016 Review.
-
Regulation of FOXO protein stability via ubiquitination and proteasome degradation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov;1813(11):1961-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.01.007. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21238503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Hippo/YAP1 signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma: From mechanisms to therapeutic drugs (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Sep;65(3):88. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5676. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39092548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-378d suppresses malignant phenotype of ESCC cells through AKT signaling.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Dec 22;21(1):702. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02403-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34937563 Free PMC article.
-
JNK and Yorkie drive tumor progression by generating polyploid giant cells in Drosophila.Oncogene. 2018 Jun;37(23):3088-3097. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0201-8. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29535423
-
cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway and Liver Disease: From Basic Research to Clinical Practice.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 18;12:719644. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.719644. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34483930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Menin directs regionalized decidual transformation through epigenetically setting PTX3 to balance FGF and BMP signaling.Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):1006. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28657-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35194044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Pinna F, Frau M, Tomasi ML, Sini M, Simile MM, Bonelli P, Muroni MR, Seddaiu MA, et al. SKP2 and CKS1 promote degradation of cell cycle regulators and are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:1816–1826. e1811–1810. - PubMed
-
- Camargo FD, Gokhale S, Johnnidis JB, Fu D, Bell GW, Jaenisch R, Brummelkamp TR. YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Current biology : CB. 2007;17:2054–2060. - PubMed
-
- Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A, Pagano M. SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nature cell biology. 1999;1:193–199. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

