Hippo Signaling Suppresses Cell Ploidy and Tumorigenesis through Skp2
- PMID: 28486106
- PMCID: PMC5863541
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.04.004
Hippo Signaling Suppresses Cell Ploidy and Tumorigenesis through Skp2
Abstract
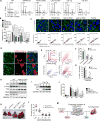
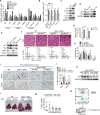
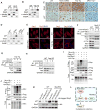
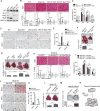
Polyploidy can lead to aneuploidy and tumorigenesis. Here, we report that the Hippo pathway effector Yap promotes the diploid-polyploid conversion and polyploid cell growth through the Akt-Skp2 axis. Yap strongly induces the acetyltransferase p300-mediated acetylation of the E3 ligase Skp2 via Akt signaling. Acetylated Skp2 is exclusively localized to the cytosol, which causes hyper-accumulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27, leading to mitotic arrest and subsequently cell polyploidy. In addition, the pro-apoptotic factors FoxO1/3 are overly degraded by acetylated Skp2, resulting in polyploid cell division, genomic instability, and oncogenesis. Importantly, the depletion or inactivation of Akt or Skp2 abrogated Hippo signal deficiency-induced liver tumorigenesis, indicating their epistatic interaction. Thus, we conclude that Hippo-Yap signaling suppresses cell polyploidy and oncogenesis through Skp2.
Keywords: Hippo; Skp2; Yap; genomic instability; p27; polyploidy; tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Pinna F, Frau M, Tomasi ML, Sini M, Simile MM, Bonelli P, Muroni MR, Seddaiu MA, et al. SKP2 and CKS1 promote degradation of cell cycle regulators and are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:1816–1826. e1811–1810. - PubMed
-
- Camargo FD, Gokhale S, Johnnidis JB, Fu D, Bell GW, Jaenisch R, Brummelkamp TR. YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Current biology : CB. 2007;17:2054–2060. - PubMed
-
- Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A, Pagano M. SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nature cell biology. 1999;1:193–199. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

