RasGRP3 Mediates MAPK Pathway Activation in GNAQ Mutant Uveal Melanoma
- PMID: 28486107
- PMCID: PMC5499527
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.04.002
RasGRP3 Mediates MAPK Pathway Activation in GNAQ Mutant Uveal Melanoma
Abstract
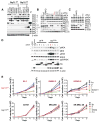
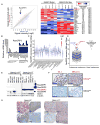
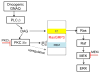
Constitutive activation of Gαq signaling by mutations in GNAQ or GNA11 occurs in over 80% of uveal melanomas (UMs) and activates MAPK. Protein kinase C (PKC) has been implicated as a link, but the mechanistic details remained unclear. We identified PKC δ and ɛ as required and sufficient to activate MAPK in GNAQ mutant melanomas. MAPK activation depends on Ras and is caused by RasGRP3, which is significantly and selectively overexpressed in response to GNAQ/11 mutation in UM. RasGRP3 activation occurs via PKC δ- and ɛ-dependent phosphorylation and PKC-independent, DAG-mediated membrane recruitment, possibly explaining the limited effect of PKC inhibitors to durably suppress MAPK in UM. The findings nominate RasGRP3 as a therapeutic target for cancers driven by oncogenic GNAQ/11.
Keywords: DAG; GNA11; GNAQ; MAPK; PKC; RasGEF; RasGRP3; melanoma; uveal melanoma.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Chen X, Resh MD. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by membrane-targeted Raf chimeras is independent of raft localization. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:3461734623. - PubMed
-
- Della Rocca GJ, van Biesen T, Daaka Y, Luttrell DK, Luttrell LM, Lefkowitz RJ. Ras-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by G protein-coupled receptors. Convergence of Gi- and Gq-mediated pathways on calcium/calmodulin, Pyk2, and Src kinase. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:1912519132. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

