Insight into runoff characteristics using hydrological modeling in the data-scarce southern Tibetan Plateau: Past, present, and future
- PMID: 28486483
- PMCID: PMC5423604
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176813
Insight into runoff characteristics using hydrological modeling in the data-scarce southern Tibetan Plateau: Past, present, and future
Abstract
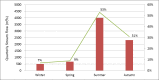
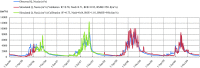
Regional hydrological modeling in ungauged regions has attracted growing attention in water resources research. The southern Tibetan Plateau often suffers from data scarcity in watershed hydrological simulation and water resources assessment. This hinders further research characterizing the water cycle and solving international water resource issues in the area. In this study, a multi-spatial data based Distributed Time-Variant Gain Model (MS-DTVGM) is applied to the Yarlung Zangbo River basin, an important international river basin in the southern Tibetan Plateau with limited meteorological data. This model is driven purely by spatial data from multiple sources and is independent of traditional meteorological data. Based on the methods presented in this study, daily snow cover and potential evapotranspiration data in the Yarlung Zangbo River basin in 2050 are obtained. Future (2050) climatic data (precipitation and air temperature) from the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC-AR5) are used to study the hydrological response to climate change. The result shows that river runoff will increase due to precipitation and air temperature changes by 2050. Few differences are found between daily runoff simulations from different Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) scenarios (RCP2.6, RCP4.5 and RCP8.5) for 2050. Historical station observations (1960-2000) at Nuxia and model simulations for two periods (2006-2009 and 2050) are combined to study inter-annual and intra-annual runoff distribution and variability. The inter-annual runoff variation is stable and the coefficient of variation (CV) varies from 0.21 to 0.27. In contrast, the intra-annual runoff varies significantly with runoff in summer and autumn accounting for more than 80% of the total amount. Compared to the historical period (1960-2000), the present period (2006-2009) has a slightly uneven intra-annual runoff temporal distribution, and becomes more balanced in the future (2050).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Sivapalan M, Takeuchi K, Franks SW, Gupta VK, Karambiri H, Lakshmi V, et al. IAHS Decade on Predictions in Ungauged Basins (PUB), 2003–2012: Shaping an exciting future for the hydrological sciences. Hydrological Sciences Journal. 2003;48(6):857–80.
-
- Sivapalan M. Prediction in ungauged basins: a grand challenge for theoretical hydrology. Hydrological Processes. 2003;17(15):3163–70.
-
- Cao J, Qin D, Kang E, Li Y. River discharge changes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chinese Science Bulletin. 2006;51(5):594–600.
-
- He C. Assessment of hydrological alterations from 1961 to 2000 in the Yarlung Zangbo River, Tibet. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology. 2012;12(2):93–103.
-
- Bamzai AS, Shukla J. Relation between Eurasian Snow Cover, Snow Depth, and the Indian Summer Monsoon: An Observational Study. Journal of Climate. 1936;12(10):3117–32.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

