Antimicrobial resistance and virulence characterization of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci from imported beef meat
- PMID: 28486995
- PMCID: PMC5424316
- DOI: 10.1186/s12941-017-0210-4
Antimicrobial resistance and virulence characterization of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci from imported beef meat
Abstract
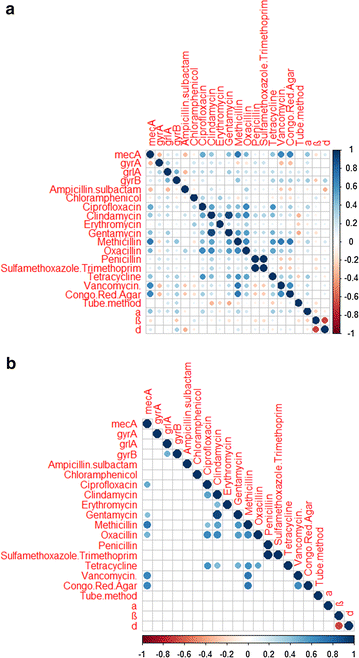
Background: The objectives of this study were to characterize the diversity and magnitude of antimicrobial resistance among Staphylococcus species recovered from imported beef meat sold in the Egyptian market and the potential mechanisms underlying the antimicrobial resistance phenotypes including harboring of resistance genes (mecA, cfr, gyrA, gyrB, and grlA) and biofilm formation.
Results: The resistance gene mecA was detected in 50% of methicillin-resistant non-Staphylococcus aureus isolates (4/8). Interestingly, our results showed that: (i) resistance genes mecA, gyrA, gyrB, grlA, and cfr were absent in Staphylococcus hominis and Staphylococcus hemolyticus isolates, although S. hominis was phenotypically resistant to methicillin (MR-non-S. aureus) while S. hemolyticus was resistant to vancomycin only; (ii) S. aureus isolates did not carry the mecA gene (100%) and were phenotypically characterized as methicillin- susceptible S. aureus (MSS); and (iii) the resistance gene mecA was present in one isolate (1/3) of Staphylococcus lugdunensis that was phenotypically characterized as methicillin-susceptible non-S. aureus (MSNSA).
Conclusions: Our findings highlight the potential risk for consumers, in the absence of actionable risk management information systems, of imported foods and advice a strict implementation of international standards by different venues such as CODEX to avoid the increase in prevalence of coagulase positive and coagulase negative Staphylococcus isolates and their antibiotic resistance genes in imported beef meat at the Egyptian market.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance genes; Coagulase-negative staphylococci; Coagulase-positive staphylococci; Imported beef meat.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methicillin resistance and biofilm production in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative Staphylococcus in México.Biomedica. 2019 Sep 1;39(3):513-523. doi: 10.7705/biomedica.4131. Biomedica. 2019. PMID: 31584765 Free PMC article. English, Spanish.
-
Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profile of Staphylococcus species in chicken and beef raw meat in Egypt.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2015 May;12(5):406-13. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2014.1882. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 25789407
-
New quadriplex PCR assay for detection of methicillin and mupirocin resistance and simultaneous discrimination of Staphylococcus aureus from coagulase-negative staphylococci.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Nov;42(11):4947-55. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.11.4947-4955.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15528678 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci: epidemiological and molecular aspects.Microbiol Immunol. 2007;51(9):787-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2007.tb03968.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17895595 Review.
-
Correlation Between Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in MRSA and MSSA Isolated from Clinical Samples in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Microb Drug Resist. 2020 Sep;26(9):1071-1080. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0001. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Microb Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32159447
Cited by
-
Epidemiological study of sausage in Algeria: Prevalence, quality assessment, and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolates and the risk factors associated with consumer habits affecting foodborne poisoning.Vet World. 2019 Aug;12(8):1240-1250. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2019.1240-1250. Epub 2019 Aug 15. Vet World. 2019. PMID: 31641303 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of florfenicol resistance genes in the coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (CoNS) isolates and genomic features of a multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus lentus strain H29.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021 Jan 7;10(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13756-020-00869-5. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021. PMID: 33413633 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of hemolysin encoding genes and their association with antimicrobial resistance pattern among clinical isolates of coagulase-negative Staphylococci.BMC Res Notes. 2020 Feb 10;13(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-4938-0. BMC Res Notes. 2020. PMID: 32041651 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Other Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci and Mammaliicoccus (MRNaS) Associated with Animals and Food Products in Arab Countries: A Review.Vet Sci. 2022 Jun 24;9(7):317. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9070317. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35878334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan and cloxacillin combination improve antibiotic efficacy against different lifestyle of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus isolates from chronic bovine mastitis.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 23;8(1):5081. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23521-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29572457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WTO 2016. World Trade Organization. Sanitary and phytosanitary measures: text of the agreement. The WTO Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS Agreement). Centre William Rappard, 154 rue de Lausanne, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Giormezis N, Kolonitsiou F, Foka A, Drougka E, Liakopoulos A, Makri A, Papanastasiou AD, Vogiatzi A, Dimitriou G, Marangos M, Christofidou M, Anastassiou ED, Petinaki E, Spiliopoulou I. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal bloodstream and prosthetic-device-associated infections: the role of biofilm formation and distribution of adhesin and toxin genes. J Med Microbiol. 2014;63:1500–1508. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.075259-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases