N-Glycosylation affects the stability and barrier function of the MUC16 mucin
- PMID: 28487369
- PMCID: PMC5491790
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.770123
N-Glycosylation affects the stability and barrier function of the MUC16 mucin
Abstract
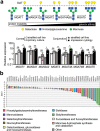
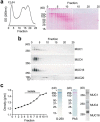
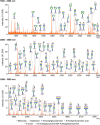
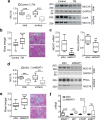
Transmembrane mucins are highly O-glycosylated glycoproteins that coat the apical glycocalyx on mucosal surfaces and represent the first line of cellular defense against infection and injury. Relatively low levels of N-glycans are found on transmembrane mucins, and their structure and function remain poorly characterized. We previously reported that carbohydrate-dependent interactions of transmembrane mucins with galectin-3 contribute to maintenance of the epithelial barrier at the ocular surface. Now, using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, we report that transmembrane mucin N-glycans in differentiated human corneal epithelial cells contain primarily complex-type structures with N-acetyllactosamine, a preferred galectin ligand. In N-glycosylation inhibition experiments, we find that treatment with tunicamycin and siRNA-mediated knockdown of the Golgi N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I gene (MGAT1) induce partial loss of both total and cell-surface levels of the largest mucin, MUC16, and a concomitant reduction in glycocalyx barrier function. Moreover, we identified a distinct role for N-glycans in promoting MUC16's binding affinity toward galectin-3 and in causing retention of the lectin on the epithelial cell surface. Taken together, these studies define a role for N-linked oligosaccharides in supporting the stability and function of transmembrane mucins on mucosal surfaces.
Keywords: N-linked glycosylation; epithelial cell; galectin; glycosyltransferase; mucin.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of cell surface mucins with galectin-3 contributes to the ocular surface epithelial barrier.J Biol Chem. 2009 Aug 21;284(34):23037-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.033332. Epub 2009 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19556244 Free PMC article.
-
The Ocular Surface Glycocalyx and its Alteration in Dry Eye Disease: A Review.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Nov 1;59(14):DES157-DES162. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-23756. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30481821 Review.
-
MUC16 mucin is expressed by the human ocular surface epithelia and carries the H185 carbohydrate epitope.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 Jun;44(6):2487-95. doi: 10.1167/iovs.02-0862. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12766047
-
A metalloproteinase secreted by Streptococcus pneumoniae removes membrane mucin MUC16 from the epithelial glycocalyx barrier.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32418. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032418. Epub 2012 Mar 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22412870 Free PMC article.
-
Role of mucins in the function of the corneal and conjunctival epithelia.Int Rev Cytol. 2003;231:1-49. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(03)31001-0. Int Rev Cytol. 2003. PMID: 14713002 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Cohort Analysis of Mutational Spectrum in Early Onset Breast Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 28;12(8):2089. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082089. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32731431 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effect of Proinflammatory Cytokines on Corneal and Conjunctival Epithelial Cell Mucins and Glycocalyx.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2021 Jun 1;10(7):17. doi: 10.1167/tvst.10.7.17. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 34128966 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolytic regulation of a galectin-3/Lrp1 axis controls osteoclast-mediated bone resorption.J Cell Biol. 2023 Apr 3;222(4):e202206121. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202206121. Epub 2023 Mar 2. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36880731 Free PMC article.
-
Restricted processing of CD16a/Fc γ receptor IIIa N-glycans from primary human NK cells impacts structure and function.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 9;293(10):3477-3489. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001207. Epub 2018 Jan 12. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29330305 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylation reduces the glycan-independent immunomodulatory effect of recombinant Orysata lectin in Drosophila S2 cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 9;11(1):17958. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97161-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34504130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGuckin M. A., Lindén S. K., Sutton P., and Florin T. H. (2011) Mucin dynamics and enteric pathogens. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 9, 265–278 - PubMed
-
- Corfield A. P. (2015) Mucins: a biologically relevant glycan barrier in mucosal protection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1850, 236–252 - PubMed
-
- Hilkens J., Ligtenberg M. J., Vos H. L., and Litvinov S. V. (1992) Cell membrane-associated mucins and their adhesion-modulating property. Trends Biochem. Sci. 17, 359–363 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

