How and why kinetics, thermodynamics, and chemistry induce the logic of biological evolution
- PMID: 28487761
- PMCID: PMC5389199
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.13.66
How and why kinetics, thermodynamics, and chemistry induce the logic of biological evolution
Abstract
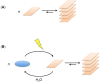
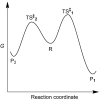
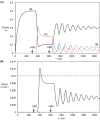
Thermodynamic stability, as expressed by the Second Law, generally constitutes the driving force for chemical assembly processes. Yet, somehow, within the living world most self-organisation processes appear to challenge this fundamental rule. Even though the Second Law remains an inescapable constraint, under energy-fuelled, far-from-equilibrium conditions, populations of chemical systems capable of exponential growth can manifest another kind of stability, dynamic kinetic stability (DKS). It is this stability kind based on time/persistence, rather than on free energy, that offers a basis for understanding the evolutionary process. Furthermore, a threshold distance from equilibrium, leading to irreversibility in the reproduction cycle, is needed to switch the directive for evolution from thermodynamic to DKS. The present report develops these lines of thought and argues against the validity of a thermodynamic approach in which the maximisation of the rate of energy dissipation/entropy production is considered to direct the evolutionary process. More generally, our analysis reaffirms the predominant role of kinetics in the self-organisation of life, which, in turn, allows an assessment of semi-quantitative constraints on systems and environments from which life could evolve.
Keywords: dynamic kinetic stability; kinetic control; origins of life; self-organisation.
Figures
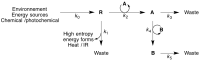
References
-
- Morowitz H J. Beginnings of cellular life – Metabolism Recapitulates Biogenesis. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press; 1992.
-
- Fry I. Biol Philos. 1995;10:389–417. doi: 10.1007/BF00857591. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
