Curcumin Inhibits NTHi-Induced MUC5AC Mucin Overproduction in Otitis Media via Upregulation of MAPK Phosphatase MKP-1
- PMID: 28487811
- PMCID: PMC5405397
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/4525309
Curcumin Inhibits NTHi-Induced MUC5AC Mucin Overproduction in Otitis Media via Upregulation of MAPK Phosphatase MKP-1
Abstract
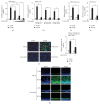
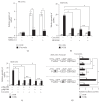
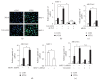
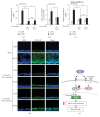
Otitis media (OM), characterized by the presence of mucus overproduction and excess inflammation in the middle ear, is the most common childhood infection. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) pathogen is responsible for approximately one-third of episodes of bacteria-caused OM. Current treatments for bacterial OM rely on the systemic use of antibiotics, which often leads to the emergence of multidrug resistant bacterial strains. Therefore there is an urgent need for developing alternative therapies strategies for controlling mucus overproduction in OM. MUC5AC mucin has been shown to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of OM. Here we show that curcumin derived from Curcuma longa plant is a potent inhibitor of NTHi-induced MUC5AC mucin expression in middle ear epithelial cells. Curcumin inhibited MUC5AC expression by suppressing activation of p38 MAPK by upregulating MAPK phosphatase MKP-1. Thus, our study identified curcumin as a potential therapeutic for inhibiting mucin overproduction in OM by upregulating MKP-1, a known negative regulator of inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphodiesterase 4B mediates extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent up-regulation of mucin MUC5AC protein by Streptococcus pneumoniae by inhibiting cAMP-protein kinase A-dependent MKP-1 phosphatase pathway.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 29;287(27):22799-811. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.337378. Epub 2012 May 18. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22610099 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin suppresses NTHi-induced CXCL5 expression via inhibition of positive IKKβ pathway and up-regulation of negative MKP-1 pathway.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 19;6:31695. doi: 10.1038/srep31695. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27538525 Free PMC article.
-
Vinpocetine inhibits Streptococcus pneumoniae-induced upregulation of mucin MUC5AC expression via induction of MKP-1 phosphatase in the pathogenesis of otitis media.J Immunol. 2015 Jun 15;194(12):5990-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401489. Epub 2015 May 13. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25972475 Free PMC article.
-
Exploitation of host epithelial signaling networks by respiratory bacterial pathogens.J Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Jan;91(1):1-7. doi: 10.1254/jphs.91.1. J Pharmacol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12686724 Review.
-
[Regulation of expression, function, and inflammatory responses of innate immune receptor Toll-like receptor-2 (TLR2) during inflammatory responses against infection].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013;133(12):1401-9. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.13-00208. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013. PMID: 24292189 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Panel 3: Genomics, precision medicine and targeted therapies.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Mar;130 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):109835. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109835. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 32007292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subversion of host immune responses by otopathogens during otitis media.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 Oct;106(4):943-956. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4RU0119-003R. Epub 2019 May 10. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 31075181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phloretin, an Apple Polyphenol, Inhibits Pathogen-Induced Mucin Overproduction.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021 Jan;65(2):e2000658. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202000658. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021. PMID: 33216464 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Evaluation of the Antimicrobial-Immunomodulatory Dual Action of Xenohormetic Molecules against Haemophilus influenzae Respiratory Infection.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 17;9(12):891. doi: 10.3390/biom9120891. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31861238 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

