TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE COMBINED WITH HORMONE THERAPY TO TREAT PREMATURE OVARIAN FAILURE: A META-ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS
- PMID: 28487907
- PMCID: PMC5416635
- DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v13i5.21
TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE COMBINED WITH HORMONE THERAPY TO TREAT PREMATURE OVARIAN FAILURE: A META-ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS
Abstract
Background: This meta-analysis aimed to provide critically estimated evidence for the advantages and disadvantages of Chinese herbal medicines used for premature ovarian failure (POF), which could provide suggestions for rational treatments.
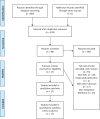
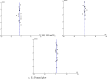
Materials and methods: The databases searched included MEDLINE, EMBASE, CNKI, VIP, China Dissertation Database, China Important Conference Papers Database, and online clinical trial registry websites. Published and unpublished randomized controlled trials of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) combined with hormone therapy (HT) and HT alone for POF were assessed up to December 30, 2015. Two authors extracted data and assessed trial quality independently using Cochrane systematic review methods. Meta-analysis was used to quantitatively describe serum hormone levels and Kupperman scores associated with perimenopause symptoms.
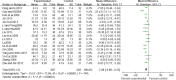
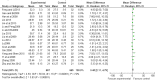
Results: Seventeen randomized controlled trials involving 1352 participants were selected. Compared with HT alone, although no significant effects were observed in the levels of luteinizing hormone, therapy with TCM combined with HT compared to HT alone effectively altered serum hormone levels of follicle stimulating hormone (P<0.01) and estradiol (P < 0.01), and improved Kupperman index scores (P< 0.01).
Conclusions: The reported favorable effects of TCM combined with HT for treating POF patients are better than HT alone.However, the beneficial effects derived from this combination therapy cannot be viewed conclusive. In order to better support the clinical use, more rigorously designed trials are required to provide.
Keywords: Hormone therapy; Meta-analysis; Premature ovarian failure; Traditional Chinese medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Clinical observation on treatment of premature ovarian failure patients of shen deficiency gan stagnation syndrome by combination of bushui roumu recipe and medroxyprogesterone acetate tablet HUA].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012 Aug;32(8):1028-31. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23173246 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Treatment of premature ovarian failure patients by bushen tiaojing recipe combined hormone replacement therapy: a clinical observation].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013 Oct;33(10):1332-5. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24432674 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
A comparison of the effects of Chinese non-pharmaceutical therapies for premature ovarian failure: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and network meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jun 26;99(26):e20958. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020958. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32590807 Free PMC article.
-
A general description for Chinese medicine in treating premature ovarian failure.Chin J Integr Med. 2017 Feb;23(2):91-97. doi: 10.1007/s11655-016-2642-7. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 28265850 Review.
-
Chinese patent medicines combined with hormone replacement therapy for premature ovarian failure: A Bayesian network meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 17;9:1043390. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1043390. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36465907 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
[Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes repair of cyclophosphamide?induced ovarian injury in rats].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2017 Dec 20;37(12):1632-1636. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2017.12.12. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 29292257 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Evidence of TCM Theory in Treating the Same Disease with Different Methods: Treatment of Pneumonia with Ephedra sinica and Scutellariae Radix as an Example.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Nov 28;2020:8873371. doi: 10.1155/2020/8873371. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33354223 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to treat premature ovarian failure.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Aug 11;12(1):454. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02529-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34380572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in premature ovarian failure: Mechanisms and prospects.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 27;13:997808. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.997808. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389844 Free PMC article.
-
Kuntai Capsule plus Hormone Therapy vs. Hormone Therapy Alone in Patients with Premature Ovarian Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Jun 26;2019:2085804. doi: 10.1155/2019/2085804. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31346337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altuntas C.Z, Johnson J.M, Tuohy V.K. Autoimmune targeted disruption of the pituitary-ovarian axis causes premature ovarian failure. The Journal of Immunology. 2006;177(7):1998–1996. - PubMed
-
- Chao S.L, Huang L.W, Yen H.R. Pregnancy in premature ovarian failure after therapy using Chinese herbal medicine. Chang Gung Medical Journal. 2003;26:449–452. - PubMed
-
- Chand A.L, Harrison C.A, Shelling A.N. Inhibin and premature ovarian failure. Human Reproduction Update. 2010;16(1):39–50. - PubMed
-
- Chen J.X, Hu L.S. Traditional Chinese medicine on the treatment of chronic prostatitis in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine. 2006;12(8):763–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
