Efficient Antibody Assembly in E. coli Periplasm by Disulfide Bond Folding Factor Co-expression and Culture Optimization
- PMID: 28488120
- PMCID: PMC5898612
- DOI: 10.1007/s12010-017-2502-8
Efficient Antibody Assembly in E. coli Periplasm by Disulfide Bond Folding Factor Co-expression and Culture Optimization
Abstract
Molecular chaperones and protein folding factors of bacterial periplasmic space play important roles in assisting disulfide bond formation and proper protein folding. In this study, effects of disulfide bond protein (Dsb) families were investigated on assembly of 3F3 Fab, an antibody inhibitor targeting matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14). By optimizing DsbA/C co-expression, promoter for 3F3 Fab, host strains, and culture media and conditions, a high yield of 30-mg purified 3F3 Fab per liter culture was achieved. Produced 3F3 Fab exhibited binding affinity of 34 nM and inhibition potency of 970 nM. This established method of DsbA/C co-expression can be applied to produce other important disulfide bond-dependent recombinant proteins in E. coli periplasm.
Keywords: DsbA; DsbC; Fab; IgG; Over-expression; Periplasm; Protein folding factor.
Figures




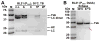
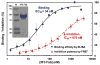
Similar articles
-
Periplasmic chaperones used to enhance functional secretion of proteins in E. coli.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;705:211-24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61737-967-3_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21125388 Review.
-
Overexpression of protein disulfide isomerase DsbC stabilizes multiple-disulfide-bonded recombinant protein produced and transported to the periplasm in Escherichia coli.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Sep;66(9):3960-5. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.9.3960-3965.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10966415 Free PMC article.
-
A system for concomitant overexpression of four periplasmic folding catalysts to improve secretory protein production in Escherichia coli.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2006 Aug;19(8):385-90. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzl018. Epub 2006 May 23. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2006. PMID: 16720693
-
DsbA and DsbC-catalyzed oxidative folding of proteins with complex disulfide bridge patterns in vitro and in vivo.J Mol Biol. 2003 Jan 17;325(3):495-513. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01248-2. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12498799
-
Disulfide Bond Formation in the Periplasm of Escherichia coli.EcoSal Plus. 2019 Feb;8(2):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0012-2018. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0012-2018. EcoSal Plus. 2019. PMID: 30761987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies for the production of isotopically labelled Fab fragments of therapeutic antibodies in Komagataella phaffii (Pichia pastoris) and Escherichia coli for NMR studies.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 29;18(11):e0294406. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294406. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38019850 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate derived sequences act as subsite-blocking motifs in protease inhibitory antibodies.Protein Sci. 2023 Jul;32(7):e4691. doi: 10.1002/pro.4691. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37278099 Free PMC article.
-
Risk assessment and bioburden evaluation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transient protein expression in plants using the CaMV35S promoter.BMC Biotechnol. 2023 Jun 7;23(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12896-023-00782-w. BMC Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37286972 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Escherichia coli Expression System in Producing Antibody Recombinant Fragments.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 31;21(17):6324. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176324. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32878291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disulfide Chaperone Knockouts Enable In Vivo Double Spin Labeling of an Outer Membrane Transporter.Biophys J. 2019 Oct 15;117(8):1476-1484. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.09.002. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Biophys J. 2019. PMID: 31582182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baneyx F, Mujacic M. Recombinant protein folding and misfolding in Escherichia coli. Nature Biotechnology. 2004;22:1399–1408. - PubMed
-
- Georgiou G, Segatori L. Preparative expression of secreted proteins in bacteria: Status report and future prospects. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 2005;16:538–545. - PubMed
-
- Schlapschy M, Skerra A. Periplasmic chaperones used to enhance functional secretion of proteins in E. coli. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2011;705:211–224. - PubMed
-
- Levy R, Weiss R, Chen G, Iverson BL, Georgiou G. Production of correctly folded Fab antibody fragment in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli trxB gor mutants via the coexpression of molecular chaperones. Protein Expression and Purification. 2001;23:338–347. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

