Efficient Antibody Assembly in E. coli Periplasm by Disulfide Bond Folding Factor Co-expression and Culture Optimization
- PMID: 28488120
- PMCID: PMC5898612
- DOI: 10.1007/s12010-017-2502-8
Efficient Antibody Assembly in E. coli Periplasm by Disulfide Bond Folding Factor Co-expression and Culture Optimization
Abstract
Molecular chaperones and protein folding factors of bacterial periplasmic space play important roles in assisting disulfide bond formation and proper protein folding. In this study, effects of disulfide bond protein (Dsb) families were investigated on assembly of 3F3 Fab, an antibody inhibitor targeting matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14). By optimizing DsbA/C co-expression, promoter for 3F3 Fab, host strains, and culture media and conditions, a high yield of 30-mg purified 3F3 Fab per liter culture was achieved. Produced 3F3 Fab exhibited binding affinity of 34 nM and inhibition potency of 970 nM. This established method of DsbA/C co-expression can be applied to produce other important disulfide bond-dependent recombinant proteins in E. coli periplasm.
Keywords: DsbA; DsbC; Fab; IgG; Over-expression; Periplasm; Protein folding factor.
Figures




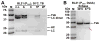
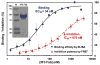
References
-
- Baneyx F, Mujacic M. Recombinant protein folding and misfolding in Escherichia coli. Nature Biotechnology. 2004;22:1399–1408. - PubMed
-
- Georgiou G, Segatori L. Preparative expression of secreted proteins in bacteria: Status report and future prospects. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 2005;16:538–545. - PubMed
-
- Schlapschy M, Skerra A. Periplasmic chaperones used to enhance functional secretion of proteins in E. coli. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2011;705:211–224. - PubMed
-
- Levy R, Weiss R, Chen G, Iverson BL, Georgiou G. Production of correctly folded Fab antibody fragment in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli trxB gor mutants via the coexpression of molecular chaperones. Protein Expression and Purification. 2001;23:338–347. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

