Uptake and Utilization of Selenium from Selenoprotein P
- PMID: 28488249
- PMCID: PMC5680150
- DOI: 10.1007/s12011-017-1044-9
Uptake and Utilization of Selenium from Selenoprotein P
Abstract
Selenoprotein P (SELENOP) is a serum glycoprotein that is required for proper selenium distribution in mammals, particularly in supplying selenium to the brain and testes. As the sole mechanism for providing essential selenium to developing spermatozoa, SELENOP metabolism is central to male fertility in all mammals. In addition, this process is important for proper brain function, especially under conditions of limited dietary selenium. Several specific and nonspecific mechanisms for SELENOP uptake in target tissues have been described, but the utilization of SELENOP as a source of selenium for intracellular selenoprotein production has not been systematically characterized. In this report, we examine the process of SELENOP uptake using a robust selenium uptake assay that measures selenium utilization in cells fed 75Se-SELENOP. Using a series of inhibitors and modulators we have identified specific regulators of the process and found that SELENOP must be in an oxidized state for uptake. This assay also demonstrates that SELENOP uptake is not highly sequence specific as the zebrafish protein is recognized and processed by mammalian cells.
Keywords: Oxidation; Selenium; Selenocysteine; Selenoprotein P.
Figures
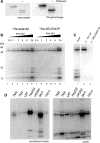
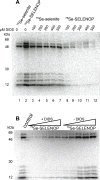
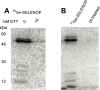
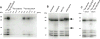

References
-
- Burk RF, Gregory PE. Some characteristics of 75Se-P, a selenoprotein found in rat liver and plasma, and comparison of it with selenoglutathione peroxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982;213(1):73–80. - PubMed
-
- Motsenbocker MA, Tappel AL. A selenocysteine-containing selenium-transport protein in rat plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982;719(1):147–153. - PubMed
-
- Motchnik PA, Tappel AL. Multiple selenocysteine content of selenoprotein P in rats. J Inorg Biochem. 1990;40(3):265–269. - PubMed
-
- Hill KE, Lloyd RS, Yang JG, Read R, Burk RF. The cDNA for rat selenoprotein P contains 10 TGA codons in the open reading frame. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(16):10050–10053. - PubMed
-
- Hill KE, Zhou J, McMahan WJ, Motley AK, Atkins JF, Gesteland RF, Burk RF. Deletion of selenoprotein P alters distribution of selenium in the mouse. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(16):13640–13646. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

