Clonidine for sedation and analgesia for neonates receiving mechanical ventilation
- PMID: 28488361
- PMCID: PMC6481534
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012468.pub2
Clonidine for sedation and analgesia for neonates receiving mechanical ventilation
Abstract
Background: Although routine administration of pharmacologic sedation or analgesia during mechanical ventilation in preterm neonates is not recommended, its use in clinical practice remains common. Alpha-2 agonists, mainly clonidine and dexmedetomidine, are used as adjunctive (or alternative) sedative agents alongside opioids and benzodiazepines. Clonidine has not been systematically assessed for use in neonatal sedation during ventilation.
Objectives: To assess whether clonidine administered to term and preterm newborn infants receiving mechanical ventilation reduces morbidity and mortality rates. To compare the intervention versus placebo, no treatment, and dexmedetomidine; and to assess the safety of clonidine infusion for potential harms.To perform subgroup analyses according to gestational age; birth weight; administration method (infusion or bolus therapy); dose, duration, and route of clonidine administration; and pharmacologic sedation as a co-intervention.
Search methods: We used the standard search strategy of the Cochrane Neonatal Review Group to search the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; 2016, Issue 12) in the Cochrane Library, MEDLINE via PubMed (1966 to January 10, 2017), Embase (1980 to January 10, 2017), and the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL; 1982 to January 10, 2017). We also searched clinical trials databases, conference proceedings, and the reference lists of retrieved articles for randomized controlled trials and quasi-randomized trials.
Selection criteria: We searched for randomized controlled trials, quasi-randomized controlled trials, and cluster trials comparing clonidine versus placebo, no treatment, or dexmedetomidine administered to term and preterm newborns receiving mechanical ventilation via an endotracheal tube.
Data collection and analysis: For the included trial, two review authors independently extracted data (e.g. number of participants, birth weight, gestational age, all-cause death during initial hospitalization, duration of respiratory support, sedation scale, duration of hospital stay) and assessed risk of bias (e.g. adequacy of randomization, blinding, completeness of follow-up). This review considered primary outcomes of all-cause neonatal death, all-cause death during initial hospitalization, and duration of mechanical ventilation in days.
Main results: One trial, which included 112 infants, met the inclusion criteria for this review. Term newborn infants on mechanical ventilation with the need for continuous analgesia and sedation with fentanyl and midazolam were eligible for enrollment during the first 96 hours of ventilation. Study authors administered clonidine 1 μg/kg/h or placebo on day 4 after intubation.We found no differences between the two groups in all-cause death during hospitalization (risk ratio [RR] 0.69, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.12 to 3.98). The quality of the evidence supporting these findings is low owing to imprecision of the estimates (one study; few events). The median (interquartile range) duration of mechanical ventilation was 7.1 days (5.7 to 9.1 days) in the clonidine group and 5.8 days (4.9 to 7.9 days) in the placebo group, respectively (P = 0.070). Among secondary outcomes, we found no differences in terms of duration of stay in the intensive care unit. Sedation scale values (COMFORT) and analgesia scores (Hartwig) during the first 72 hours of infusion of study medication were lower in the clonidine group than in the placebo group.
Authors' conclusions: At present, evidence is insufficient to show the efficacy and safety of clonidine for sedation and analgesia in term and preterm newborn infants receiving mechanical ventilation.
Conflict of interest statement
OR, MGC, EN, and MB declare no known conflicts of interest.
Figures
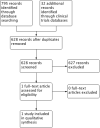



Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Hünseler 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hünseler C, Balling G, Röhlig C, Blickheuser R, Trieschmann U, Lieser U, et al. Clonidine Study Group. Continuous infusion of clonidine in ventilated newborns and infants: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 2014;15(6):511‐22. [DOI: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000151; PUBMED: 24751788 ] - DOI - PubMed
Additional references
Anand 1987a
Anand 1987b
-
- Anand KJ, Sippell WG, Aynsley‐Green A. Randomised trial of fentanyl anaesthesia in preterm babies undergoing surgery: effects on the stress response. Lancet 1987;1(8524):62‐6. [PUBMED: 2879174 ] - PubMed
Anand 1999
-
- Anand KJ, Barton BA, McIntosh N, Lagercrantz H, Pelausa E, Young TE, et al. Analgesia and sedation in preterm neonates who require ventilatory support: results from the NOPAIN trial. Neonatal Outcome and Prolonged Analgesia in Neonates. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 1999;153(4):331‐8. [PUBMED: 10201714 ] - PubMed
Anand 2004
-
- Anand KJ, Hall RW, Desai N, Shephard B, Bergqvist LL, Young TE, et al. NEOPAIN Trial Investigators Group. Effects of morphine analgesia in ventilated preterm neonates: primary outcomes from the NEOPAIN randomised trial. Lancet 2004;363(9422):1673‐82. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16251-X; PUBMED: 15158628 ] - DOI - PubMed
Bayley 1993
-
- Bayley N. Bayley Scales of Infant Development. 2nd Edition. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation, 1993.
Bayley 2006
-
- Bayley N. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development. 3rd Edition. San Antonio, TX: Harcourt Assessment, 2006.
Bellieni 2005
-
- Bellieni CV, Bagnoli F, Sisto R, Neri L, Cordelli D, Buonocore G. Development and validation of the ABC pain scale for healthy full‐term babies. Acta Paediatrica 2005;94(10):1432‐6. [PUBMED: 16299876 ] - PubMed
Bellù 2008
Carbajal 1997
-
- Carbajal R, Paupe A, Hoenn E, Lenclen R, Olivier‐Martin M. APN: evaluation behavioral scale of acute pain in newborn infants. Archives de Pediatrie 1997;4(7):623‐8. [PUBMED: 9295899 ] - PubMed
Carbajal 2005
Chen 2015
Clark 2006
Cochrane EPOC 2013
-
- Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). Data extraction and management. EPOC resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, 2013. epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors.
Cornette 2002
-
- Cornette LG, Tanner SF, Ramenghi LA, Miall LS, Childs AM, Arthur RJ, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the infant brain: anatomical characteristics and clinical significance of punctate lesions. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Edition 2002;86(3):F171‐7. [PUBMED: 11978747] - PMC - PubMed
de Graaf 2011
-
- Graaf J, Lingen RA, Simons SH, Anand KJ, Duivenvoorden HJ, Weisglas‐Kuperus N, et al. Long‐term effects of routine morphine infusion in mechanically ventilated neonates on children’s functioning: five‐year follow‐up of a randomized controlled trial. Pain 2011;152(6):1391‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2011.02.017; PUBMED: 21402444 ] - DOI - PubMed
Debillon 2001
Duffett 2012
Egger 1997
Ferguson 2012
-
- Ferguson SA, Ward WL, Paule MG, Hall RW, Anand KJ. A pilot study of preemptive morphine analgesia in preterm neonates: effects on head circumference, social behavior, and response latencies in early childhood. Neurotoxicology and Teratology 2012;34(1):47‐55. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ntt.2011.10.008; PUBMED: 22094261 ] - DOI - PubMed
Fitzgerald 1986
-
- Fitzgerald M, Koltzenburg M. The functional development of descending inhibitory pathways in the dorsolateral funiculus of the newborn rat spinal cord. Brain Research 1986;389(1‐2):261‐70. [PUBMED: 3948011 ] - PubMed
Gibbins 2014
Gold 1978
-
- Gold M, Redmond DE, Kleber H. Clonidine blocks acute opiate‐withdrawal symptoms. Lancet 1978;2(8090):599‐602. [PUBMED: 80526 ] - PubMed
Golianu 2007
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- Grade Working Group, McMaster University. GRADEpro [www.gradepro.org]. Version Version 14 September 2014. Hamilton (ON): Grade Working Group, McMaster University, 2014.
Graça 2013
Gregoretti 2009
-
- Gregoretti C, Moglia B, Pelosi P, Navalesi P. Clonidine in perioperative medicine and intensive care unit: more than an anti‐hypertensive drug. Current Drug Targets 2009;10(8):799‐814. [PUBMED: 19702526 ] - PubMed
Griffiths 1954
-
- Griffiths R. The Abilities of Babies: A Study in Mental Measurement. New York, NY: McGraw‐Hill Book Co. Inc., 1954.
Grunau 1986
-
- Grunau RE, Oberlander T, Holsti L, Whitfield MF. Bedside application of the Neonatal Facial Coding System in pain assessment of premature neonates. Pain 1986;76(3):277‐86. [PUBMED: 9718246 ] - PubMed
Hall 2007
Hammer 1989
-
- Hammer RP Jr, Ricalde AA, Seatriz JV. Effects of opiates on brain development. Neurotoxicology 1989;10(3):475‐83. [PUBMED: 2696899] - PubMed
Handelmann 1985
-
- Handelmann GE, Dow‐Edwards D. Modulation of brain development by morphine: effects on central motor systems and behavior. Peptides 1985;6(Suppl 2):29‐34. [PUBMED: 4080616] - PubMed
Hayden 2016
Hazell 2003
-
- Hazell PL, Stuart JE. A randomized controlled trial of clonidine added to psychostimulant medication for hyperactive and aggressive children. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2003;42(8):886‐94. [DOI: 10.1097/01.CHI.0000046908.27264.00; PUBMED: 12874489] - DOI - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. handbook.cochrane.org.
Hodgkinson 1994
-
- Hodgkinson K, Bear M, Thorn J, Blaricum S. Measuring pain in neonates: evaluating an instrument and developing a common language. Australian Journal of Advanced Nursing 1994;12(1):17‐22. [PUBMED: 7786451] - PubMed
Hoy 2011
Hummel 2010
Hünseler 2011
Ibrahim 2016
ICROP 1984
-
- Committee for the Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity. An international classification of retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatrics 1984;74(1):127‐33. [PUBMED: 6547526] - PubMed
Ista 2005
Jacobs 2013
Jacqz‐Aigrain 1994
-
- Jacqz‐Aigrain E, Daoud P, Burtin P, Desplanques L, Beaufils F. Placebo‐controlled trial of midazolam sedation in mechanically ventilated newborn babies. Lancet 1994;344(8923):646‐50. [PUBMED: 7915348] - PubMed
Jamadarkhana 2010
Jing Wang 2015
Jobe 2001
Kumar 2008
Lago 1998
Lambert 2014
Laudenbach 2002
-
- Laudenbach V, Mantz J, Lagercrantz H, Desmonts JM, Evrard P, Gressens P. Effects of alpha(2)‐adrenoceptor agonists on perinatal excitotoxic brain injury: comparison of clonidine and dexmedetomidine. Anesthesiology 2002;96(1):134‐41. [PUBMED: 11753013] - PubMed
Lawrence 1993
-
- Lawrence J, Alcock D, McGrath P, Kay J, MacMurray SB, Dulberg C. The development of a tool to assess neonatal pain. Neonatal Network 1993;12(6):59‐66. [PUBMED: 8413140] - PubMed
Limperopoulos 2007
-
- Limperopoulos C, Bassan H, Gauvreau K, Robertson RL Jr, Sullivan NR, Benson CB, et al. Does cerebellar injury in premature infants contribute to the high prevalence of long‐term cognitive, learning, and behavioral disability in survivors?. Pediatrics 2007;120(3):584‐93. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2007-1041; PUBMED: 17766532] - DOI - PubMed
Lundqvist 2014
Ma 2007
Mantz 2011
Mason 2011
McPherson 2007
Milesi 2010
-
- Milesi C, Cambonie G, Jacquot A, Barbotte E, Mesnage R, Masson F, et al. Validation of a neonatal pain scale adapted to the new practices in caring for preterm newborns. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Edition 2010;95(4):F263‐6. [DOI: 10.1136/adc.2008.144758; PUBMED: 19221401] - DOI - PubMed
Ng 2017
NIH 1979
-
- National Institutes of Health. Report of Workshop on Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia; December 4‐6, 1978. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; Division of Lung Diseases, 1979. Report No.: 80‐1660.
Nishina 1999
-
- Nishina K, Akamatsu H, Mikawa K, Shiga M, Maekawa N, Obara H, et al. The effects of clonidine and dexmedetomidine on human neutrophil functions. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1999;88(2):424‐8. [PUBMED: 9972773 ] - PubMed
O'Mara 2009
O'Mara 2012
-
- O'Mara K, Gal P, Wimmer J, Ransom JL, Carlos RQ, Dimaguila MA, et al. Dexmedetomidine versus standard therapy with fentanyl for sedation in mechanically ventilated premature neonates. Journal of Pediatric Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2012;17(3):252‐62. [DOI: 10.5863/1551-6776-17.3.252; PUBMED: 23258968] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Papile 1978
-
- Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. Journal of Pediatrics 1978;92(4):529‐34. [PUBMED: 305471] - PubMed
Paris 2006
Parodi 2015
Peters 2003
-
- Peters JW, Koot HM, Grunau RE, Boer J, Druenen MJ, Tibboel D, et al. Neonatal Facial Coding System for assessing postoperative pain in infants: item reduction is valid and feasible. Clinical Journal of Pain 2003;19(6):353‐63. [PUBMED: 14600535] - PubMed
Pichot 2012
Pontén 2012
Revman 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Ricalde 1990
-
- Ricalde AA, Hammer RP Jr. Perinatal opiate treatment delays growth of cortical dendrites. Neuroscience Letters 1990;115(2‐3):137‐43. [PUBMED: 2172870] - PubMed
Riker 2009
-
- Riker RR, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Ceraso D, Wisemandle W, Koura F, et al. SEDCOM (Safety and Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine Compared With Midazolam) Study Group. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for sedation of critically ill patients: a randomized trial. JAMA 2009;301(5):489‐99. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2009.56; DOI: ] - DOI - PubMed
Ruokonen 2009
-
- Ruokonen E, Parviainen I, Jakob SM, Nunes S, Kaukonen M, Shepherd ST, et al. "Dexmedetomidine for Continuous Sedation" Investigators. Dexmedetomidine versus propofol/midazolam for long‐term sedation during mechanical ventilation. Intensive Care Medicine 2009;35(2):282‐90. [DOI: 10.1007/s00134-008-1296-0; PUBMED: 18795253] - DOI - PubMed
Rutherford 2010
Schünemann 2013
-
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editors. GRADE Working Group. GRADE Handbook for Grading Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations. https://gdt.gradepro.org/app/handbook/handbook.html. Updated October 2013.
Seatriz 1993
-
- Seatriz JV, Hammer RP Jr. Effects of opiates on neuronal development in the rat cerebral cortex. Brain Research Bulletin 1993;30(5‐6):523‐7. [PUBMED: 8384517 ] - PubMed
Sheng 2015
Simons 2003
Stefovska 2008
Stevens 1996
-
- Stevens B, Johnston C, Petryshen P, Taddio A. Premature Infant Pain Profile: development and initial validation. Clinical Journal of Pain 1996;12(1):13‐22. [PUBMED: 8722730] - PubMed
Taddio 2009
Taniguchi 2004
-
- Taniguchi T, Kidani Y, Kanakura H, Takemoto Y, Yamamoto K. Effects of dexmedetomidine on mortality rate and inflammatory responses to endotoxin‐induced shock in rats. Critical Care Medicine 2004;32(6):1322‐6. [PUBMED: 15187514] - PubMed
Taniguchi 2008
Tasdogan 2009
-
- Tasdogan M, Memis D, Sut N, Yuksel M. Results of a pilot study on the effects of propofol and dexmedetomidine on inflammatory responses and intraabdominal pressure in severe sepsis. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2009;21(6):394‐400. [PUBMED: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2008.10.010; PUBMED: 19833271] - PubMed
van Dijk 2009
-
- Dijk M, Roofthooft DW, Anand KJ, Guldemond F, Graaf J, Simons S, et al. Taking up the challenge of measuring prolonged pain in (premature) neonates: the COMFORTneo scale seems promising. The Clinical Journal of Pain 2009;25(7):607‐16. [DOI: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181a5b52a; PUBMED: 19692803] - DOI - PubMed
Virtanen 1988
-
- Virtanen R, Savola JM, Saano V, Nyman L. Characterization of the selectivity, specificity and potency of medetomidine as an alpha 2‐adrenoceptor agonist. European Journal of Pharmacology 1988;150(1‐2):9‐14. [PUBMED: 2900154] - PubMed
Walsh 2004
-
- Walsh MC, Yao Q, Gettner P, Hale E, Collins M, Hensman A, et al. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Impact of a physiologic definition on bronchopulmonary dysplasia rates. Pediatrics 2004;114(5):1305‐11. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2004-0204; PUBMED: 15520112] - DOI - PubMed
Young 2005
-
- Young C, Jevtovic‐Todorovic V, Qin YQ, Tenkova T, Wang H, Labruyere J, et al. Potential of ketamine and midazolam, individually or in combination, to induce apoptotic neurodegeneration in the infant mouse brain. British Journal of Pharmacology 2005;146(2):189‐97. [DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706301; PUBMED: 15997239] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Zagon 1977
-
- Zagon IS, McLaughlin PJ. Morphine and brain growth retardation in the rat. Pharmacology 1977;15(3):276‐82. [PUBMED: 866403] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

