The c.797 G>A (p.R266K) cystathionine β-synthase mutation causes homocystinuria by affecting protein stability
- PMID: 28488385
- PMCID: PMC5525156
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.23240
The c.797 G>A (p.R266K) cystathionine β-synthase mutation causes homocystinuria by affecting protein stability
Abstract
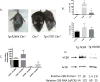
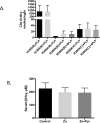
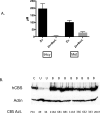
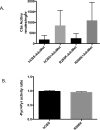
Mutations in the cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS) gene are the cause of classical homocystinuria, the most common inborn error in sulfur metabolism. The c.797 G>A (p.R266K) mutation in CBS was originally described in several Norwegian pyridoxine responsive CBS deficient patients, and heterologous gene expression studies have shown that the protein has near wild-type levels of enzyme activity. Here, we characterize a transgenic mouse lacking endogenous Cbs and expressing p.R266K human CBS protein from a zinc inducible metallothionein promoter (Tg-R266K Cbs-/- ). Unlike mice expressing other mutant CBS alleles, the Tg-R266K transgene is unable to efficiently rescue neonatal lethality of Cbs-/- on a C57BL/6J background. On a C3H/HeJ background, zinc-induced Tg-R266K Cbs-/- mice express CBS mRNA, but have very low levels of CBS protein and enzyme activity, resulting in extreme elevations in serum total homocysteine (tHcy). Treatment with pyridoxine did not have any appreciable effect on tHcy, indicating this allele is not pyridoxine responsive in mice. However, treatment with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib resulted in an 97% reduction in tHcy and a 2381% increase in liver CBS activity. These studies show that the p.R266K mutation causes increased proteasomal degradation in vivo, and that treatments that stabilize the protein can be used to reverse its effect.
Keywords: CBS; bortezomib; homocysteine; methionine; pyridoxine.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Akahoshi N, Kobayashi C, Ishizaki Y, Izumi T, Himi T, Suematsu M, Ishii I. Genetic background conversion ameliorates semi-lethality and permits behavioral analyses in cystathionine beta-synthase-deficient mice, an animal model for hyperhomocysteinemia. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:1994–2005. - PubMed
-
- Balch WE, Morimoto RI, Dillin A, Kelly JW. Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention. Science. 2008;319:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Wang L, Fazlieva R, Kruger WD. Contrasting behaviors of mutant cystathionine beta-synthase enzymes associated with pyridoxine response. Hum Mutat. 2006;27:474–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

