Chalcone: A Privileged Structure in Medicinal Chemistry
- PMID: 28488435
- PMCID: PMC6131713
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00020
Chalcone: A Privileged Structure in Medicinal Chemistry
Abstract
Privileged structures have been widely used as an effective template in medicinal chemistry for drug discovery. Chalcone is a common simple scaffold found in many naturally occurring compounds. Many chalcone derivatives have also been prepared due to their convenient synthesis. These natural products and synthetic compounds have shown numerous interesting biological activities with clinical potentials against various diseases. This review aims to highlight the recent evidence of chalcone as a privileged scaffold in medicinal chemistry. Multiple aspects of chalcone will be summarized herein, including the isolation of novel chalcone derivatives, the development of new synthetic methodologies, the evaluation of their biological properties, and the exploration of the mechanisms of action as well as target identification. This review is expected to be a comprehensive, authoritative, and critical review of the chalcone template to the chemistry community.
Conflict of interest statement
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


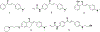
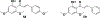
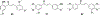
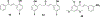

















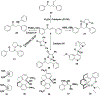

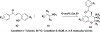
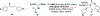
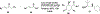



References
-
- Batovska DI; Todorova IT Trends in utilization of the pharmacological potential of chalcones. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol 2010, 5, 1–29. - PubMed
-
- Sahu NK; Balbhadra SS; Choudhary J; Kohli DV Exploring pharmacological significance of chalcone scaffold: a review. Curr. Med. Chem 2012, 19, 209–225. - PubMed
-
- Singh P; Anand A; Kumar V Recent developments in biological activities of chalcones: a mini review. Eur. J. Med. Chem 2014, 85, 758–777. - PubMed
-
- Karthikeyan C; Moorthy NS; Ramasamy S; Vanam U; Manivannan E; Karunagaran D; Trivedi P Advances in chalcones with anticancer activities. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery 2015, 10, 97–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

