Wrist cineradiography: a protocol for diagnosing carpal instability
- PMID: 28488457
- PMCID: PMC5791518
- DOI: 10.1177/1753193417694820
Wrist cineradiography: a protocol for diagnosing carpal instability
Abstract
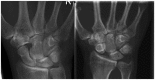
Carpal instability is often related to ruptured or lax carpal ligaments. Wrist cineradiography has been shown to be a good modality for diagnosing carpal instability. To create uniformity in obtaining and assessing wrist cineradiography, a wrist cineradiography protocol is desirable. This protocol will focus on wrist cineradiography for diagnosing carpal instabilities. It describes the pathologic motions of the carpus and correlates these with a clinical diagnosis.
Level of evidence: III.
Keywords: Carpal instability; fluoroscopy; scapholunate dissociation; scapholunate ligament; wrist cineradiography.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Arkless R. Cineradiography in normal and abnormal wrists. AJR. 1966, 96: 837–44. - PubMed
-
- Böttcher R, Mutze S, Lautenbach M, Eisenschenk A. Diagnosis of lunotriquetral instability. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2005, 37: 131–6. - PubMed
-
- Brink PRG, Bransz N, Deijkers RLM, et al. Dutch guideline for distal radius fractures: diagnoses and treatment. Utrecht, The Netherlands, Nederlandse Vereniging voor Heelkunde, 2010.
-
- Garcia-Elias M. The treatment of wrist instability. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997, 79: 684–90. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Elias M. The non-dissociative clunking wrist: a personal view. J Hand Surg Eur. 2008, 33: 698–711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

