Hypomorphic conditional deletion of E11/Podoplanin reveals a role in osteocyte dendrite elongation
- PMID: 28488815
- PMCID: PMC5575468
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25999
Hypomorphic conditional deletion of E11/Podoplanin reveals a role in osteocyte dendrite elongation
Abstract
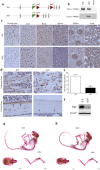
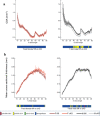
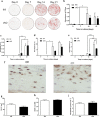
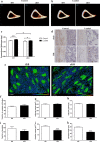
The transmembrane glycoprotein E11/Podoplanin (Pdpn) has been implicated in the initial stages of osteocyte differentiation. However, its precise function and regulatory mechanisms are still unknown. Due to the known embryonic lethality induced by global Pdpn deletion, we have herein explored the effect of bone-specific Pdpn knockdown on osteocyte form and function in the post-natal mouse. Extensive skeletal phenotyping of male and female 6-week-old Oc-cre;Pdpnflox/flox (cKO) mice and their Pdpnflox/flox controls (fl/fl) has revealed that Pdpn deletion significantly compromises tibial cortical bone microarchitecture in both sexes, albeit to different extents (p < 0.05). Consistent with this, we observed an increase in stiffness in female cKO mice in comparison to fl/fl mice (p < 0.01). Moreover, analysis of the osteocyte phenotype by phalloidin staining revealed a significant decrease in the dendrite volume (p < 0.001) and length (p < 0.001) in cKO mice in which deletion of Pdpn also modifies the bone anabolic loading response (p < 0.05) in comparison to age-matched fl/fl mice. Together, these data confirm a regulatory role for Pdpn in osteocyte dendrite formation and as such, in the control of osteocyte function. As the osteocyte dendritic network is known to play vital roles in regulating bone modeling/remodeling, this highlights an essential role for Pdpn in bone homeostasis.
Keywords: E11; dendrite; osteoblasts; osteocalcin; osteocytes.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Physiology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Balemans, W. , Ebeling, M. , Patel, N. , Van Hul, E. , Olson, P. , Dioszegi, M. , … Van Hul, W. (2001). Increased bone density in sclerosteosis is due to the deficiency of a novel secreted protein (SOST). Human Molecular Genetics, 10, 537–543. - PubMed
-
- Cao, Y. X. , Ramirez, M. I. , & Williams, M. C. (2003). Enhanced binding of Sp1/Sp3 transcription factors mediates the hyperoxia‐induced increased expression of the lung type I cell gene T1alpha. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 89, 887–901. - PubMed
-
- De Souza, R. L. , Matsuura, M. , Eckstein, F. , Rawlinson, S. C. , Lanyon, L. E. , & Pitsillides, A. A. (2005). Non‐invasive axial loading of mouse tibiae increases cortical bone formation and modifies trabecular organization: A new model to study cortical and cancellous compartments in a single loaded element. Bone, 37, 810–818. - PubMed
-
- Dobbs, L. G. , Williams, M. C. , & Gonzalez, R. (1988). Monoclonal antibodies specific to apical surfaces of rat alveolar type I cells bind to surfaces of cultured, but not freshly isolated, type II cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 970, 146–156. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

