Development of bioanalytical assays for variegin, a peptide-based bivalent direct thrombin inhibitor
- PMID: 28488882
- PMCID: PMC6040050
- DOI: 10.4155/bio-2017-0006
Development of bioanalytical assays for variegin, a peptide-based bivalent direct thrombin inhibitor
Abstract
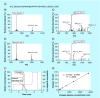
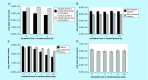
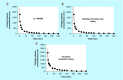
Aim: Variegin is an anticoagulant peptide that will be tested in porcine models of percutaneous coronary intervention. We developed three bioanalytical assays for variegin quantitation and utilized these methods to evaluate pharmacokinetics of variegin in pigs. Results & methodology: The LC-MS/MS, thrombin amidolytic and modified thrombin time assays had a quantitation range of 21.6-5541.7, 10.8-5541.7 and 5.4-5541.7 nM in human plasma, respectively. The elimination half-lives obtained using the LC-MS/MS, modified thrombin time and thrombin amidolytic assays were 52.3 ± 4.4, 50.4 ± 5.9 and 67.7 ± 6.3 min, respectively.
Conclusion: We developed three bioanalytical assays for a novel direct thrombin inhibitor, variegin. The thrombin time assay is optimized for variegin quantitation during future porcine studies and clinical trials.
Keywords: LC–MS/MS; anticoagulant; bioanalytical assays; thrombin amidolytic assay; thrombin time.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by a grant from the NMRC, Singapore (NMRC/CIRG/1399/2014). MY Chan receives salary support from an NMRC Clinician-Scientist Award (CSAINV15may011). The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Miesbach W, Seifried E. New direct oral anticoagulants current therapeutic options and treatment recommendations for bleeding complications. Thromb. Haemost. 2012;108(4):625–632. - PubMed
-
- van Es N, Bleker SM, Buller HR, Coppens M. New developments in parenteral anticoagulation for arterial and venous thromboembolism. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2013;26(2):203–213. - PubMed
-
- Hirsh J, Anand SS, Halperin JL, Fuster V American Heart Association. Guide to anticoagulant therapy: heparin: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2001;103(24):2994–3018. - PubMed
-
- Di Nisio M, Middeldorp S, Büller HR. Direct thrombin inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;353(10):1028–1040. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
