Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and Treatment With a Biologic: A Case Report
- PMID: 28488978
- PMCID: PMC5424646
- DOI: 10.7812/TPP/16-060
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and Treatment With a Biologic: A Case Report
Abstract
Introduction: One of the most dangerous dermatologic emergencies is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)/toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). Although a rare disease, it can often lead to significant mortality.
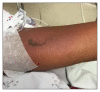
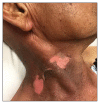
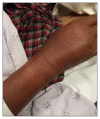
Case presentation: In this case report, we present a 77-year-old man who developed a sloughing rash that was secondary to a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. In addition to the recommended supportive care, the patient was treated with etanercept, a new, less commonly used intervention.
Discussion: We provide a brief review of SJS/TEN. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are a rare cause of SJS/TEN, and additionally, the use of biologics is a novel treatment modality for SJS/TEN.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Ward KE, Archambault R, Mersfelder TL. Severe adverse skin reactions to nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: A review of the literature. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2010 Feb 1;67(3):206–13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp080603. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Morelli MS, O’Brien FX. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and cholestatic hepatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2001 Nov;46(11):2385–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012351231143. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roujeau JC, Kelly JP, Naldi L, et al. Medication use and the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. N Engl J Med. 1995 Dec 14;333(24):1600–7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199512143332404. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gerull R, Nelle M, Schaible T. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: A review. Crit Care Med. 2011 Jun;39(6):1521–32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e31821201ed. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stevens AM, Johnson FC. A new eruptive fever associated with stomatitis and ophthalmia: Report of two cases in children. Am J Dis Child. 1922 Dec;24(6):526–33. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.1922.04120120077005. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

