Mechanically-Guided Deterministic Assembly of 3D Mesostructures Assisted by Residual Stresses
- PMID: 28489315
- PMCID: PMC5559729
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.201700151
Mechanically-Guided Deterministic Assembly of 3D Mesostructures Assisted by Residual Stresses
Abstract
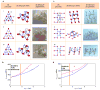
Formation of 3D mesostructures in advanced functional materials is of growing interest due to the widespread envisioned applications of devices that exploit 3D architectures. Mechanically guided assembly based on compressive buckling of 2D precursors represents a promising method, with applicability to a diverse set of geometries and materials, including inorganic semiconductors, metals, polymers, and their heterogeneous combinations. This paper introduces ideas that extend the levels of control and the range of 3D layouts that are achievable in this manner. Here, thin, patterned layers with well-defined residual stresses influence the process of 2D to 3D geometric transformation. Systematic studies through combined analytical modeling, numerical simulations, and experimental observations demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed strategy through ≈20 example cases with a broad range of complex 3D topologies. The results elucidate the ability of these stressed layers to alter the energy landscape associated with the transformation process and, specifically, the energy barriers that separate different stable modes in the final 3D configurations. A demonstration in a mechanically tunable microbalance illustrates the utility of these ideas in a simple structure designed for mass measurement.
Keywords: 3D mesostructures; compressive buckling; microbalance; mode transition; residual stress.
© 2017 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A mechanically driven form of Kirigami as a route to 3D mesostructures in micro/nanomembranes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 22;112(38):11757-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515602112. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26372959 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanically Guided Hierarchical Assembly of 3D Mesostructures.Adv Mater. 2022 Mar;34(12):e2109416. doi: 10.1002/adma.202109416. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Adv Mater. 2022. PMID: 35067974
-
Engineered elastomer substrates for guided assembly of complex 3D mesostructures by spatially nonuniform compressive buckling.Adv Funct Mater. 2017 Jan 5;27(1):1604281. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201604281. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Adv Funct Mater. 2017. PMID: 28970775 Free PMC article.
-
Colloidal Materials for 3D Printing.Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2019 Jun 7;10:17-42. doi: 10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-060718-030133. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2019. PMID: 30951639 Review.
-
Mechanically-Guided 3D Assembly for Architected Flexible Electronics.Chem Rev. 2023 Sep 27;123(18):11137-11189. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00335. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Chem Rev. 2023. PMID: 37676059 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prospective Design, Rapid Prototyping, and Testing of Smart Dressings, Drug Delivery Patches, and Replacement Body Parts Using Microscopy Aided Design and ManufacturE (MADAME).Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Dec 13;5:348. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00348. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30619859 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of biological systems with electronic-mechanical assemblies.Acta Biomater. 2019 Sep 1;95:91-111. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.04.032. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31004844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postbuckling analyses of frame mesostructures consisting of straight ribbons for mechanically guided three-dimensional assembly.Proc Math Phys Eng Sci. 2019 May;475(2225):20190012. doi: 10.1098/rspa.2019.0012. Epub 2019 May 29. Proc Math Phys Eng Sci. 2019. PMID: 31236053 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and opportunities in engineering next-generation 3D microelectronic devices: improved performance and higher integration density.Nanoscale Adv. 2024 Sep 26;6(24):6044-6060. doi: 10.1039/d4na00578c. eCollection 2024 Dec 3. Nanoscale Adv. 2024. PMID: 39569337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the interface mechanics of hard films and soft substrates for 3D assembly by controlled buckling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jul 30;116(31):15368-15377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1907732116. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31315983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Valentine J, Zhang S, Zentgraf T, Ulin-Avila E, Genov DA, Bartal G, Zhang X. Nature. 2008;455:376. - PubMed
-
- Schaedler TA, Jacobsen AJ, Torrents A, Sorensen AE, Lian J, Greer JR, Valdevit L, Carter WB. Science. 2011;334:962. - PubMed
-
- Zheng X, Lee H, Weisgraber TH, Shusteff M, DeOtte J, Duoss EB, Kuntz JD, Biener MM, Ge Q, Jackson JA, Kucheyev SO, Fang NX, Spadaccini CM. Science. 2014;344:1373. - PubMed
-
- Jang D, Meza LR, Greer F, Greer JR. Nat Mater. 2013;12:893. - PubMed
-
- Cho JH, Keung MD, Verellen N, Lagae L, Moshchalkov VV, Van Dorpe P, Gracias DH. Small. 2011;7:1943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

