Analysis of STAT3 post-translational modifications (PTMs) in human prostate cancer with different Gleason Score
- PMID: 28489571
- PMCID: PMC5522088
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17245
Analysis of STAT3 post-translational modifications (PTMs) in human prostate cancer with different Gleason Score
Abstract
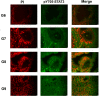
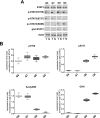
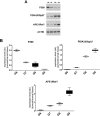
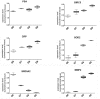
Prostate Cancer (PCa) is a complex and heterogeneous disease. The androgen receptor (AR) and the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) could be effective targets for PCa therapy. STAT3, a cytoplasmatic latent transcription factor, is a hub protein for several oncogenic signalling pathways and up-regulates the expression of numerous genes involved in tumor cell proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis and cell survival. STAT3 activity can be modulated by several Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs) which reflect particular cell conditions and may be implicated in PCa development and progression. The aim of this work was to analyze STAT3 PTMs at different tumor stages and their relationship with STAT3 cellular functions. For this purpose, sixty-five prostatectomy, Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) specimens, classified with different Gleason Scores, were subjected to immunoblotting, immunofluorescence staining and RT-PCR analysis. All experiments were carried out in matched non-neoplastic and neoplastic tissues. Data obtained showed different STAT3 PTMs profiles among the analyzed tumor grades which correlate with differences in the amount and distribution of specific STAT3 interactors as well as the expression of STAT3 target genes. These results highlight the importance of PTMs as an additional biomarker for the exactly evaluation of the PCa stage and the optimal treatment of this disease.
Keywords: PTMs; STAT3; biomarkers; prostate cancer; signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist
Figures
References
-
- Tabayoyong W, Abouassaly R. Prostate Cancer Screening and the Associated Controversy. Surg Clin North Am. 2015;95:1023–39. - PubMed
-
- Pinsky PF, Andriole G, Crawford ED, Chia D, Kramer BS, Grubb R, Greenlee R, Gohagan JK. Prostate-specific antigen velocity and prostate cancer gleason grade and stage. Cancer. 2007;109:1689–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

