Oleate-induced PTX3 promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through the up-regulation of vimentin
- PMID: 28489600
- PMCID: PMC5522334
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17326
Oleate-induced PTX3 promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through the up-regulation of vimentin
Abstract
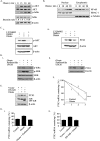
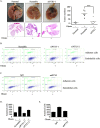
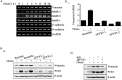
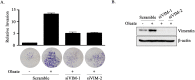
The association between metabolic diseases and the risk of developing cancer is emerging. However, the impact of long pentraxin-3 (PTX3) on dyslipidemia-associated tumor metastasis remains unknown. In this study, we found that oleate induced PTX3 expression and secretion through the activation of Akt/NF-κB pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs). The activation of NF-κB was essential for the oleate-induced stabilization of PTX3 mRNA. In addition, both the depletion of PTX3 and the inhibition of NF-κB significantly inhibited oleate-induced tumor cell migration and invasion. The enhancement of binding between tumor and endothelial cells was observed in oleate-treated cells but not in the depletion and neutralization of PTX3 with siPTX3 and anti-PTX3 antibodies, respectively. The levels of oleate-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers, such as vimentin and MMP-3, were significantly reduced in PTX3-depleted cells. Knocking down vimentin also repressed oleate-induced HNSCC invasion. Furthermore, the depletion of PTX3 blocked the oleate-primed metastatic seeding of tumor cells in the lungs. These results demonstrate that oleate enhances HNSCC metastasis through the PTX3/vimentin signaling axes. The inhibition of PTX3 could be a potential strategy for the treatment of dyslipidemia-mediated HNSCC metastasis.
Keywords: PTX3; metastasis; oleate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Forastiere A, Koch W, Trotti A, Sidransky D. Head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1890–1900. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho AL, Nishimoto IN, Califano JA, Kowalski LP. Trends in incidence and prognosis for head and neck cancer in the United States: a site-specific analysis of the SEER database. Int J Cancer. 2005;114:806–816. - PubMed
-
- Fidler IJ. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the 'seed and soil' hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:453–458. - PubMed
-
- Hursting SD, Hursting MJ. Growth signals, inflammation, and vascular perturbations: mechanistic links between obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cancer. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32:1766–1770. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

