Rectal cancer: Short-term reproducibility of intravoxel incoherent motion parameters in 3.0T magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 28489784
- PMCID: PMC5428618
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006866
Rectal cancer: Short-term reproducibility of intravoxel incoherent motion parameters in 3.0T magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
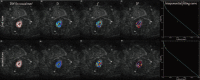
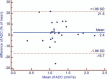
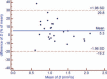
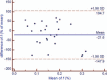
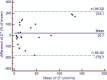
The aim of this study was to evaluate the short-term test-retest reproducibility of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) parameters of rectal cancer with 3.0T MRI.Twenty-six patients with rectal cancer underwent MRI, including diffusion-weighted imaging with 8 b values. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) parameters (D, pure diffusion; f, perfusion fraction; D*, pseudodiffusion coefficient) were, respectively, calculated. The short-term test-retest reproducibility, the intra and interobserver variation of the IVIM parameters were assessed based on the repeatability coefficient and Bland-Altman limits of agreement.There was no significant intra or interobserver difference observed in the parameters on the same DW-MRI scan. The corresponding repeatability coefficient of intra- and interobserver analysis for ADC, D, f, and D* was 5.4%, 11.1%, 55.4%, and 40.3%; 10.9%, 41.6%, 134.0%, and 177.6%, respectively. The test-retest repeatability coefficient for ADC, D, f, and D* was 19.1%, 24.5%, 126.3%, and 197.4%, respectively, greater than the intraobserver values.ADC and D have better short-term test-retest reproducibility than f and D*. Considering the poor test-retest reproducibility for f and D,* variance in these 2 parameters should be interpreted with caution in longitudinal studies on rectal cancer in which treatment response and recurrence are monitored.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hötker AM, Garcia-Aguilar J, Gollub MJ. Multiparametric MRI of rectal cancer in the assessment of response to therapy: a systematic review. Dis Colon Rectum 2014;57:790–9. - PubMed
-
- Curvo-Semedo L, Lambregts DM, Maas M, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI in rectal cancer: apparent diffusion coefficient as a potential noninvasive marker of tumor aggressiveness. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012;35:1365–71. - PubMed
-
- Elmi A, Hedgire SS, Covarrubias D, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient as a non-invasive predictor of treatment response and recurrence in locally advanced rectal cancer. Clin Radiol 2013;68:e524–31. - PubMed
-
- Jung SH, Heo SH, Kim JW, et al. Predicting response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer: diffusion-weighted 3 tesla MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012;35:110–6. - PubMed
-
- Koh DM, Collins DJ, Orton MR. Intravoxel incoherent motion in body diffusion-weighted MRI: reality and challenges. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011;196:1351–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

