Recruitment of macrophages from the spleen contributes to myocardial fibrosis and hypertension induced by angiotensin II
- PMID: 28490219
- PMCID: PMC5843916
- DOI: 10.1177/1470320317706653
Recruitment of macrophages from the spleen contributes to myocardial fibrosis and hypertension induced by angiotensin II
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to determine whether macrophages migrated from the spleen are associated with angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis and hypertension.
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to angiotensin II infusion in vehicle (500 ng/kg/min) for up to four weeks. In splenectomy, the spleen was removed before angiotensin II infusion. In the angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockade, telmisartan was administered by gastric gavage (10 mg/kg/day) during angiotensin II infusion. The heart and aorta were isolated for Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry.
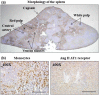
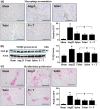
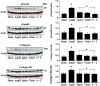
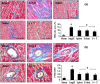
Results: Angiotensin II infusion caused a significant reduction in the number of monocytes in the spleen through the AT1 receptor-activated monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Comparison of angiotensin II infusion, splenectomy and telmisartan comparatively reduced the recruitment of macrophages into the heart. Associated with this change, transforming growth factor β1 expression and myofibroblast proliferation were inhibited, and Smad2/3 and collagen I/III were downregulated. Furthermore, interstitial/perivascular fibrosis was attenuated. These modifications occurred in coincidence with reduced blood pressure. At week 4, invasion of macrophages and myofibroblasts in the thoracic aorta was attenuated and expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase was upregulated, along with a reduction in aortic fibrosis.
Conclusions: These results suggest that macrophages when recruited into the heart and aorta from the spleen potentially contribute to angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis and hypertension.
Keywords: Angiotensin II AT1 receptor; collagen; hypertension; macrophages; myocardial fibrosis; splenectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Edaravone inhibits pressure overload-induced cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction by reducing expression of angiotensin II AT1 receptor.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Oct 16;11:3019-3033. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S144807. eCollection 2017. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017. PMID: 29081650 Free PMC article.
-
Preservation of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Level Attenuates Angiotensin II-Induced Tissue Fibrosis by Altering AT1/AT 2 Receptor Expression and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Activity in Rat Heart.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2015 Jun;29(3):243-55. doi: 10.1007/s10557-015-6592-7. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2015. PMID: 25994830
-
Angiotensin II AT1 receptor alters ACE2 activity, eNOS expression and CD44-hyaluronan interaction in rats with hypertension and myocardial fibrosis.Life Sci. 2016 May 15;153:141-52. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.04.013. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27085217
-
Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein/aldosterone synthase mediates angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Feb;47(2):1207-1222. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-05222-7. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 31820314
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1: a key mediator of angiotensin II-induced target organ damage in hypertensive heart disease?J Hypertens. 2004 Mar;22(3):451-4. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000098211.37783.e7. J Hypertens. 2004. PMID: 15076146 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP2 regulates pro-fibrogenic monocyte infiltration and activity in heart fibrosis.Nat Commun. 2022 Nov 30;13(1):7375. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34971-6. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36450710 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Key Genes from the Visceral Adipose Tissues of Overweight/Obese Adults with Hypertension through Transcriptome Sequencing.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2022;162(10):541-559. doi: 10.1159/000528702. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2022. PMID: 36521430 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in fibrosis.Matrix Biol. 2020 Sep;91-92:92-108. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2020.04.005. Epub 2020 May 16. Matrix Biol. 2020. PMID: 32422329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory responses mediate brain-heart interaction after ischemic stroke in adult mice.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020 Jun;40(6):1213-1229. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18813317. Epub 2018 Nov 22. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020. PMID: 30465612 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory and Molecular Pathways in Heart Failure-Ischemia, HFpEF and Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 10;20(9):2322. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092322. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31083399 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cesta MF. Normal structure, function, and histology of the spleen. Toxicol Pathol 2006; 34: 455–465. - PubMed
-
- van der Laan AM, Hirsch A, Robbers LF, et al. A proinflammatory monocyte response is associated with myocardial injury and impaired functional outcome in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: Monocytes and myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 2012; 163: 57–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

