Molecular remodeling of the renin-angiotensin system after kidney transplantation
- PMID: 28490223
- PMCID: PMC5843863
- DOI: 10.1177/1470320317705232
Molecular remodeling of the renin-angiotensin system after kidney transplantation
Abstract
Objective: We aimed at assessing the molecular adaptation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) after successful kidney transplantation (KTX).
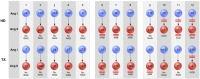
Materials and methods: In this prospective, exploratory study we analyzed 12 hemodialysis (HD) patients, who received a KTX and had excellent graft function six to 12 months thereafter. The concentrations of plasma Angiotensin (Ang) peptides (Ang I, Ang II, Ang-(1-7), Ang-(1-5), Ang-(2-8), Ang-(3-8)) were simultaneously quantified with a novel mass spectrometry-based method. Further, renin and aldosterone concentrations were determined by standard immunoassays.
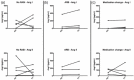
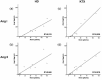
Results: Ang values showed a strong inter-individual variability among HD patients. Yet, despite a continued broad dispersion of Ang values after KTX, a substantial improvement of the renin/Ang II correlation was observed in patients without RAS blockade or on angiotensin receptor blocker (HD: renin/Ang II R2 = 0.660, KTX: renin/Ang II R2 = 0.918). Ang-(1-7) representing the alternative RAS axis was only marginally detectable both on HD and after KTX.
Conclusions: Following KTX, renin-dependent Ang II formation adapts in non-ACE inhibitor-treated patients. Thus, a largely normal RAS regulation is reconstituted after successful KTX. However, individual Ang concentration variations and a lack of potentially beneficial alternative peptides after KTX call for individualized treatment. The long-term post-transplant RAS regulation remains to be determined.
Keywords: Renin-angiotensin system; angiotensin; blood pressure; hemodialysis; kidney transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Opelz G, Zeier M, Laux G, et al. No improvement of patient or graft survival in transplant recipients treated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers: A collaborative transplant study report. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 3257–3262. - PubMed
-
- Heinze G, Collins S, Benedict MA, et al. The association between angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker use during postischemic acute transplant failure and renal allograft survival. Transplantation 2006; 82: 1441–1448. - PubMed
-
- Hernández D, Muriel A, Abraira V, et al. Renin-angiotensin system blockade and kidney transplantation: A longitudinal cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012; 27: 417–422. - PubMed
-
- Stigant CE, Cohen J, Vivera M, et al. ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II antagonists in renal transplantation: An analysis of safety and efficacy. Am J Kidney Dis 2000; 35: 58–63. - PubMed
-
- Glicklich D, Gordillo R, Supe K, et al. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor use soon after renal transplantation: A randomized, double-blinded placebo-controlled safety study. Clin Transplant 2011; 25: 843–848. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

