Cochlear implant electrode sealing techniques and related intracochlear pressure changes
- PMID: 28490377
- PMCID: PMC5426068
- DOI: 10.1186/s40463-017-0218-y
Cochlear implant electrode sealing techniques and related intracochlear pressure changes
Abstract
Background: The inserted cochlear implanted electrode is covered at the site of the round window or cochleostomy to prevent infections and leakage. In a surgically hearing preservational concept, low intracochlear pressure changes are of high importance. The aim of this study was to observe intracochlear pressure changes due to different sealing techniques in a cochlear model.
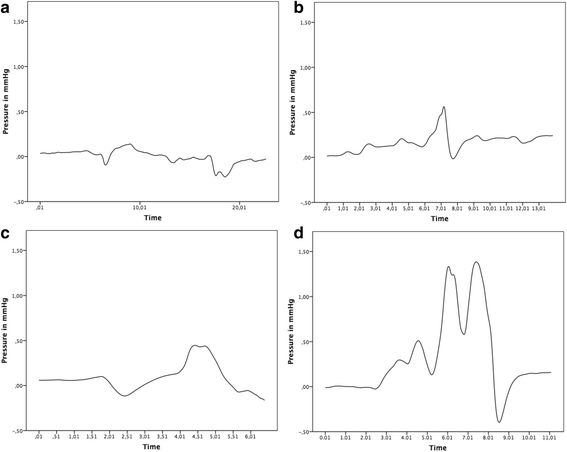
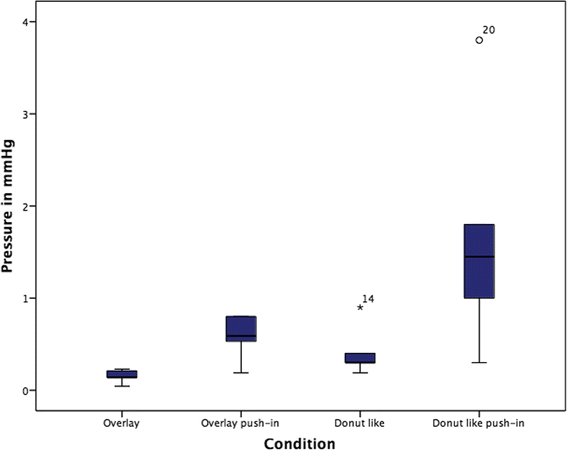
Methods: Cochlear implant electrode insertions were performed in an artifical cochlear model and the intracochlear pressure changes were recorded in parallel with a micro-pressure sensor positioned in the apical region of the cochlea model to follow the maximum amplitude of intracochlear pressure. Four different sealing conditions were compared: 1) overlay, 2) overlay with fascia pushed in, 3) donut-like fascia ring, 4) donut-like fascia ring pushed in.
Results: We found statistically significant differences in the occurrence of maximum amplitude of intracochlear pressure peak changes related to sealing procedure comparing the different techniques. While the lowest amplitude changes could be observed for the overlay technique (0.14 mmHg ± 0.06) the highest values could be observed for the donut-like pushed in technique (1.79 mmHg ± 0.69).
Conclusion: Sealing the electrode inserted cochlea can lead to significant intracochlear pressure changes. Pushing in of the sealing tissue cannot be recommended.
Keywords: Cochlea implant; Intracochlear pressure; Round window; Sealing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Different Insertion Techniques of a Cochlear Implant Electrode on the Intracochlear Pressure.Audiol Neurootol. 2016;21(1):30-7. doi: 10.1159/000442041. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Audiol Neurootol. 2016. PMID: 26794906
-
Postinsertional Cable Movements of Cochlear Implant Electrodes and Their Effects on Intracochlear Pressure.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:3937196. doi: 10.1155/2016/3937196. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27900329 Free PMC article.
-
Optimisation of the round window opening in cochlear implant surgery in wet and dry conditions: impact on intracochlear pressure changes.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Nov;273(11):3609-3613. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-3993-6. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26993657
-
Potential benefits from deeply inserted cochlear implant electrodes.Ear Hear. 2011 Jul-Aug;32(4):411-27. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0b013e3182064bda. Ear Hear. 2011. PMID: 21248642 Review.
-
Outcomes review of modern hearing preservation technique in cochlear implant.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2016 Oct;43(5):485-8. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2016.02.014. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2016. PMID: 26976547 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute effects of cochleostomy and electrode-array insertion on compound action potentials in normal-hearing guinea pigs.Front Neurosci. 2023 Feb 8;17:978230. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.978230. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36845413 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Underwater Insertion on Intracochlear Pressure.Front Surg. 2020 Nov 30;7:546779. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2020.546779. eCollection 2020. Front Surg. 2020. PMID: 33425980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Todt I, Ernst A, Mittmann P. Effects of round window opening size and moisturised electrodes on intracochlear pressure related to the insertion of a cochlear implant electrode. Audiol Neurotol Extra. 2016;6:1–8. doi: 10.1159/000442515. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

