Adipokine Contribution to the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 28490838
- PMCID: PMC5401756
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/5468023
Adipokine Contribution to the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis
Abstract
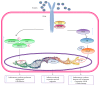
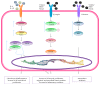
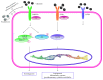
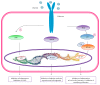
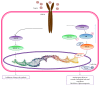
Recent studies have shown that overweight and obesity play an important role in the development of osteoarthritis (OA). However, joint overload is not the only risk factor in this disease. For instance, the presence of OA in non-weight-bearing joints such as the hand suggests that metabolic factors may also contribute to its pathogenesis. Recently, white adipose tissue (WAT) has been recognized not only as an energy reservoir but also as an important secretory organ of adipokines. In this regard, adipokines have been closely associated with obesity and also play an important role in bone and cartilage homeostasis. Furthermore, drugs such as rosuvastatin or rosiglitazone have demonstrated chondroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects in cartilage explants from patients with OA. Thus, it seems that adipokines are important factors linking obesity, adiposity, and inflammation in OA. In this review, we are focused on establishing the physiological mechanisms of adipokines on cartilage homeostasis and evaluating their role in the pathophysiology of OA based on evidence derived from experimental research as well as from clinical-epidemiological studies.
Figures
References
-
- Hart D. J., Doyle D. V., Spector T. D. Association between metabolic factors and knee osteoarthritis in women: the Chingford study. The Journal of Rheumatology. 1995;22(6):1118–1123. - PubMed
-
- Parimisetty A., Dorsemans A. C., Awada R., Ravanan P., Diotel N., Lefebvre d'Hellencourt C. Secret talk between adipose tissue and central nervous system via secreted factors-an emerging frontier in the neurodegenerative research. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2016;13(1):p. 67. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0530-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

