Protective efficacy of a single salvianolic acid A treatment on photothrombosis-induced sustained spatial memory impairments
- PMID: 28490880
- PMCID: PMC5414628
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S127094
Protective efficacy of a single salvianolic acid A treatment on photothrombosis-induced sustained spatial memory impairments
Abstract
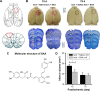
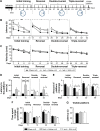
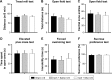
With respect to the high burden of ischemic stroke and the absence of pharmacological treatment for promoting rehabilitation, promising candidates with specific effects on long-term functional recovery are highly desired. Candidates need reasonable experimental paradigms to evaluate the long-term functional outcome focused on ischemia-induced sensorimotor and memory deficits. "Danshen", a traditional Chinese herb, has long been used to treat coronary and cerebral vascular diseases as well as dementia. Salvianolic acid A (SAA), one of the major active ingredients of Danshen, was demonstrated to be effective in protecting against cerebral ischemic injury. Here, employing an experimental stroke model induced by photothrombosis in the unilateral frontal cortex of rats, we investigated whether SAA has long-term protective effects on ischemia-induced sensorimotor and memory deficits in our behavioral tests. The results indicated that a single SAA treatment improved the cortical ischemia-induced sensorimotor deficits during 15 days' cylinder test period, and alleviated ischemia-induced sustained spatial memory impairments during the 2 months' dependent Morris Water Maze (MWM) tests. In addition, either ischemic injury or SAA treatment did not show any changes compared with sham group in other behavioral tests including rotarod tests, swimming speed in MWM tests, open field tests, elevated plus maze tests, treadmill tests and forced swimming tests. The results reveal that the cognitive deficits are not the results of animal's anxiety or confounding motor impairments. Overall, the present paradigm appears suitable for the preclinical evaluation of the long-term effects of pharmacological treatments on ischemic stroke. Meanwhile, SAA might have therapeutic potential for the treatment of memory deficits associated with ischemic stroke.
Keywords: dementia; ischemic stroke; memory impairments; salvianolic acid A.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Arboix A, Alio J. Acute cardioembolic stroke: an update. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2011;9(3):367–379. - PubMed
-
- Fisher M. New approaches to neuroprotective drug development. Stroke. 2011;42(1 Suppl):S24–S27. - PubMed
-
- Stroke Therapy Academic Industry Roundtable (STAIR) Recommendations for standards regarding preclinical neuroprotective and restorative drug development. Stroke. 1999;30(12):2752–2758. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

