Narrowband ultraviolet B light treatment changes plasma concentrations of MMP-3, MMP-9 and TIMP-3 in psoriatic patients
- PMID: 28490884
- PMCID: PMC5414720
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S125595
Narrowband ultraviolet B light treatment changes plasma concentrations of MMP-3, MMP-9 and TIMP-3 in psoriatic patients
Abstract
Background: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) are thought to be associated with the pathogenesis and spread of psoriatic disease. This study was designed to investigate the plasma levels of MMP-3, MMP-9 and TIMP-3 in plaque psoriasis patients prior to and following a course of ultraviolet B narrowband treatment with respect to disease advancement.
Methods: Plasma samples of 49 patients suffering from plaque psoriasis and 40 healthy volunteers were evaluated. Concentrations of MMP-3, MMP-9 and TIMP-3 were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, while Psoriasis Area and Severity Index was used to define disease advancement.
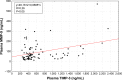
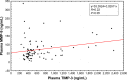
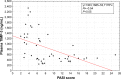
Results: Plasma levels of MMP-3, MMP-9 and TIMP-3 were significantly elevated in psoriasis patients compared to healthy individuals. A course of ultraviolet B narrowband treatment resulted in a significant decline in the studied metalloproteinases. Furthermore, the concentration of selected tissue inhibitors was negatively correlated with baseline Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score.
Conclusion: Our research highlights the meaningful role of MMP-3, MMP-9 and TIMP-3 in psoriasis pathogenesis and clearance of disease symptoms. Furthermore, plasma levels of the analyzed metalloproteinases seem to be a valuable psoriasis biomarker.
Keywords: gelatinase B; stromelysin 1.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Gooderham MJ, Poulin-Costello M, Shelton J, Bayan N, Papp KA. Predictors of topical use in psoriasis patients in the REFINE Study. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016;20(2):106–112. - PubMed
-
- Parisi R, Symmons DPM, Griffiths CEM, et al. Global epidemiology of psoriasis: a systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133:377–385. - PubMed
-
- Cohen BE, Martires KJ, Ho RS. Psoriasis and the risk of depression in the US population: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009–2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152(1):73–79. - PubMed
-
- Huerta C, Rivero E, Rodríguez LA. Incidence and risk factors for psoriasis in the general population. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143(12):1559–1565. - PubMed
-
- Boehncke WH. Etiology and pathogenesis of psoriasis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2015;41(4):665–675. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

