Chemoprotective effect of omega-3 fatty acids on thioacetamide induced hepatic fibrosis in male rats
- PMID: 28490971
- PMCID: PMC5415165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.01.029
Chemoprotective effect of omega-3 fatty acids on thioacetamide induced hepatic fibrosis in male rats
Abstract
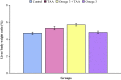
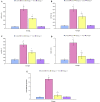
The current study was designed to investigate the possible protective effect of omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil on hepatic fibrosis induced by thioacetamide (TAA) in male rats. The experimental animals were divided into four groups. The first group was received saline solution and served as control. The second group was given 250 mg/kg body weight of TAA. The third group was treated with omega-3 fatty acids and TAA. The fourth group was given saline solution and supplemented with omega-3 fatty acids. Treatment of rats with TAA for three and six weeks resulted in a significant decrease in body weight gain, while the value of liver/body weight ratio was statistically increased. Furthermore, the levels of serum alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, gamma glutamyl transferase and total bilirubin were significantly increased. After three weeks of exposure to only TAA, liver sections showed an abnormal morphology characterized by noticeable fibrosis with the extracellular matrix collagen contents and damage of liver cells' structure. Liver sections from rats treated with only TAA for six weeks revealed an obvious increase in extracellular matrix collagen content and bridging fibrosis. Treating TAA-intoxicated rats with omega-3 fatty acids significantly attenuated the severe physiological and histopathological changes. Finally, the present investigation suggests that omega-3 fatty acids could act against hepatic fibrosis induced by TAA due to its antioxidant properties, thus supporting its use in hepatic fibrosis therapy.
Keywords: Hepatic fibrosis; Omega-3 fatty acids; Rats; Thioacetamide.
Figures






References
-
- Abdou S.E., Taha N.M., Mandour A.A., Lebda M.A., El Hofi H.R., El-Morshedy A.M.S.E. Antifibrotic effect of curcumin on thioacetamide induced liver fibrosis. Alexandria J. Vet. Sci. 2015;45:43–50.
-
- Abramovitch S., Sharvit E., Weisman Y., Bentov A., Brazowski E., Cohen G., Volovelsky O., Reif S. Vitamin D inhibits development of liver fibrosis in an animal model but cannot ameliorate established cirrhosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015;308:G112–G120. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed O.M. Histopathological and biochemical evaluation of liver and kidney lesions in streptozotocin diabetic rats treated with glimepiride and various plant extracts. J. Union Arab Biol. 2001;16A:585–625.
-
- Alaraj M., Qiblawi S. Protective effects of fish oil on carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in rabbits. Int. J. Sci. Basic Appl. Res. 2015;19:400–408.
-
- Al-Attar A.M. Physiological effects of some plant oils supplementation on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Res. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2010;5:55–71.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

