Opinion: Inhibition of Blood-Brain Barrier Repair as a Mechanism in HIV-1 Disease
- PMID: 28491017
- PMCID: PMC5405129
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00228
Opinion: Inhibition of Blood-Brain Barrier Repair as a Mechanism in HIV-1 Disease
Keywords: HIV-1; NMDAR; Tat; VEGFR; blood-brain barrier (BBB); c-Src.
Figures
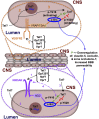
References
-
- Andras I. E., Deli M. A., Veszelka S., Hayashi K., Hennig B., Toborek M. (2007). The NMDA and AMPA/KA receptors are involved in glutamate-induced alterations of occludin expression and phosphorylation in brain endothelial cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 27, 1431–1443. 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600445 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

