Association between Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Heart Rate Variability in Adults at Increased Cardiovascular Risk
- PMID: 28491040
- PMCID: PMC5405141
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00248
Association between Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Heart Rate Variability in Adults at Increased Cardiovascular Risk
Abstract
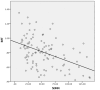
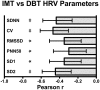
Background: Atherosclerotic carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) may be associated with alterations in the sensitivity of carotid baroreceptors. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between carotid IMT and the autonomic modulation of heart rate variability (HRV). Methods: A total of 101 subjects were enrolled in this prospective observational study. The carotid IMT was determined by duplex ultrasonography. The cardiac autonomic function was determined through HRV measures during the Deep Breathing Test. Linear regression models, adjusted for demographics, comorbidities, body mass index, waist-hip-ratio, and left ventricular ejection fraction were used to evaluate the association between HRV parameters and carotid IMT. Results: Participants had a mean age of 60.4 ± 13.4 years and an estimated 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk score (using the Pooled Cohort Equations) of 16.4 ± 17. The mean carotid media thickness was highest (0.90 ± 0.19 mm) in the first quartile of the standard deviation of all RR intervals (SDNN) (19.7 ± 5.1 ms) and progressively declined in each subsequent quartile to 0.82 ± 0.21 mm, 0.81 ± 0.16 mm, and 0.68 ± 0.19 in quartiles 2 (36.5 ± 5.9 ms), 3 (57.7 ± 6.2 ms) and 4 (100.9 ± 22.2 ms), respectively. In multivariable adjusted models, there was a statistical significant association between SDNN and carotid IMT (OR -0.002; 95%CI -0.003 to -0.001, p = 0.005). The same significant association was found between carotid IMT and other measures of HRV, including coefficient of variation of RR intervals (CV) and dispersion of points along the line of identity (SD2). Conclusions: In a cohort of individuals at increased cardiovascular risk, carotid IMT as a marker of subclinical atherosclerosis was associated with alterations of HRV indicating an impaired cardiac autonomic control, independently of other cardiovascular risk factors.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cardiovagal; carotid; deep breathing test; heart rate/heart rate variability.
Figures
References
-
- (1996). Assessment: clinical autonomic testing report of the therapeutics and technology assessment subcommittee of the american academy of neurology. Neurology 46, 873–880. - PubMed
-
- Bonyhay I., Jokkel G., Kollai M. (1996). Relation between baroreflex sensitivity and carotid artery elasticity in healthy humans. Am. J. Physiol. 271(3 Pt 2), H1139–H1144. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

