Identification of Genes Controlled by the Essential YycFG Two-Component System Reveals a Role for Biofilm Modulation in Staphylococcus epidermidis
- PMID: 28491057
- PMCID: PMC5405149
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00724
Identification of Genes Controlled by the Essential YycFG Two-Component System Reveals a Role for Biofilm Modulation in Staphylococcus epidermidis
Abstract
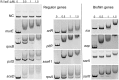
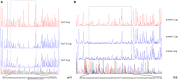
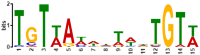
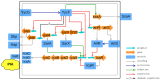
Biofilms play a crucial role in the pathogenicity of Staphylococcus epidermidis, while little is known about whether the essential YycFG two-component signal transduction system (TCS) is involved in biofilm formation. We used antisense RNA (asRNA) to silence the yycFG TCS in order to study its regulatory functions in S. epidermidis. Strain 1457 expressing asRNA yycF exhibited a significant delay (~4-5 h) in entry to log phase, which was partially complemented by overexpressing ssaA. The expression of asRNA yycF and asRNA yycG resulted in a 68 and 50% decrease in biofilm formation at 6 h, respectively, while they had no significant inhibitory effect on 12 h biofilm formation. The expression of asRNA yycF led to a ~5-fold increase in polysaccharide intercellular adhesion (PIA) production, but it did not affect the expression of accumulation-associated protein (Aap) or the release of extracellular DNA. Consistently, quantitative real-time PCR showed that silencing yycF resulted in an increased transcription of biofilm-related genes, including icaA, arlR, sarA, sarX, and sbp. An in silico search of the YycF regulon for the conserved YycF recognition pattern and a modified motif in S. epidermidis, along with additional gel shift and DNase I footprinting assays, showed that arlR, sarA, sarX, and icaA are directly regulated by YycF. Our data suggests that YycFG modulates S. epidermidis biofilm formation in an ica-dependent manner.
Keywords: Staphylococcus epidermidis; YycFG; antisense RNA; biofilm; two-component signal transduction system.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Role of Staphylococcus aureus YycFG in Gene Regulation, Biofilm Organization and Drug Resistance.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Dec 19;10(12):1555. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10121555. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the two-component regulatory system arlRS in ica operon and aap positive but non-biofilm-forming Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates from hospitalized patients.Microb Pathog. 2014 Nov;76:89-98. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2014.09.013. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Microb Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25263000
-
Antisense yycG Regulation of Antibiotic Sensitivity of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Chronic Osteomyelitis.Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2019 Sep;20(6):472-479. doi: 10.1089/sur.2019.016. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2019. PMID: 31038392
-
An Antisense yycF RNA Modulates Biofilm Organization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pathogenicity in a Rat Model of Osteomyelitis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 May 19;10(5):603. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10050603. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34069543 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in biofilm: structural and regulatory aspects.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Feb 10;5:7. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00007. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25713785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of biofilm formation by Enterococcus faecalis isolates derived from urinary tract infections in China.J Med Microbiol. 2018 Jan;67(1):60-67. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000647. J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29148361 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus PhoU Homologs Regulate Persister Formation and Virulence.Front Microbiol. 2020 May 26;11:865. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00865. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32670206 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Analysis Reveals a Biofilm-Like Behavior of Planktonic Aggregates of Staphylococcus epidermidis Grown Under Environmental Pressure/Stress.Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 6;10:1909. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01909. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31551940 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Staphylococcus aureus YycFG in Gene Regulation, Biofilm Organization and Drug Resistance.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Dec 19;10(12):1555. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10121555. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems: A Major Strategy for Connecting Input Stimuli to Biofilm Formation.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jan 10;9:3279. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03279. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30687268 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al Laham N., Rohde H., Sander G., Fischer A., Hussain M., Heilmann C., et al. . (2007). Augmented expression of polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in a defined Staphylococcus epidermidis mutant with the small-colony-variant phenotype. J. Bacteriol. 189, 4494–4501. 10.1128/JB.00160-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bateman B. T., Donegan N. P., Jarry T. M., Palma M., Cheung A. L. (2001). Evaluation of a tetracycline-inducible promoter in Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo and its application in demonstrating the role of sigB in microcolony formation. Infect. Immun. 69, 7851–7857. 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7851-7857.2001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

