Familial long QT syndrome and late development of dilated cardiomyopathy in a child with a KCNQ1 mutation: A case report
- PMID: 28491650
- PMCID: PMC5412615
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrcr.2015.10.011
Familial long QT syndrome and late development of dilated cardiomyopathy in a child with a KCNQ1 mutation: A case report
Keywords: Dilated cardiomyopathy; Familial long QT syndrome; Genetics; KCNQ1; Voltage-gated potassium channel.
Figures
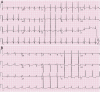
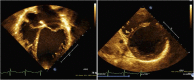

Similar articles
-
A founder mutation of the potassium channel KCNQ1 in long QT syndrome: implications for estimation of disease prevalence and molecular diagnostics.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001 Feb;37(2):562-8. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(00)01124-4. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001. PMID: 11216980
-
A double-point mutation in the selectivity filter site of the KCNQ1 potassium channel results in a severe phenotype, LQT1, of long QT syndrome.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2008 May;19(5):541-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2007.01076.x. Epub 2008 Feb 4. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18266681
-
Induced KCNQ1 autoimmunity accelerates cardiac repolarization in rabbits: potential significance in arrhythmogenesis and antiarrhythmic therapy.Heart Rhythm. 2014 Nov;11(11):2092-100. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2014.07.040. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Heart Rhythm. 2014. PMID: 25087487
-
The molecular genetics of the long QT syndrome: genes causing fainting and sudden death.Annu Rev Med. 1998;49:263-74. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.49.1.263. Annu Rev Med. 1998. PMID: 9509262 Review.
-
KCNQ1 gene mutations and the respective genotype-phenotype correlations in the long QT syndrome.Med Sci Monit. 2002 Oct;8(10):RA240-8. Med Sci Monit. 2002. PMID: 12388934 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular studies in familial dilated cardiomyopathy - A pilot study.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022 Apr 11;40:101023. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2022.101023. eCollection 2022 Jun. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2022. PMID: 35463915 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden Cardiac Arrest in the Postpartum Period Due to Long QT Syndrome and Dilated Cardiomyopathy.JACC Case Rep. 2023 May 16;16:101882. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2023.101882. eCollection 2023 Jun 21. JACC Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37396328 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of CCR4-NOT complex subunits affects heart structure and function.Dis Model Mech. 2020 Jul 20;13(7):dmm044727. doi: 10.1242/dmm.044727. Dis Model Mech. 2020. PMID: 32471864 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Ion Channels in Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID): Evidence of Channelopathies and Potential Avenues for Future Research and Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 4;24(13):11074. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311074. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446251 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McNair W.P., Sinagra G., Taylor M.R., Di Lenarda A., Ferguson D.A., Salcedo E.E., Slavov D., Zhu X., Caldwell J.H., Mestroni L. SCN5A mutations associate with arrhythmic dilated cardiomyopathy and commonly localize to the voltage-sensing mechanism. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:2160–2168. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kwon H.W., Lee S.Y., Kwon B.S., Kim G.B., Bae E.J., Kim W.H., Noh C.I., Cho S.I., Park S.S. Long QT syndrome and dilated cardiomyopathy with SCN5A p.R1193Q polymorphism: cardioverter-defibrillator implantation at 27 months. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2012;35:e243–e246. - PubMed
-
- Shi R., Zhang Y., Yang C., Huang C., Zhou X., Qiang H., Grace A.A., Huang C.L., Ma A. The cardiac sodium channel mutation delQKP 1507-1509 is associated with the expanding phenotypic spectrum of LQT3, conduction disorder, dilated cardiomyopathy, and high incidence of youth sudden death. Europace. 2008;10:1329–1335. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

