Pemetrexed-induced acute kidney failure following irreversible renal damage: two case reports and literature review
- PMID: 28491851
- PMCID: PMC5418068
- DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2017.07
Pemetrexed-induced acute kidney failure following irreversible renal damage: two case reports and literature review
Abstract
Background: Pemetrexed (PEM) is a new-generation multitargeted antifolate agent with a demonstrated broad-spectrum activity in several types of human cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and mesothelioma. Major side effects include dose-limiting hematologic toxicities. PEM nephrotoxicity is well known; however, its frequency is considered to be low.
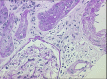
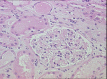
Case presentation: Here we report two cases of acute kidney injury (AKI) related to PEM administration (500 mg/m2) in patients with NSCLC. The first patient required hemodialysis treatment and was submitted to renal biopsy which showed acute tubular damage and interstitial edema without acute tubular necrosis. No other potential nephrotoxic agents were identified. The second patient developed AKI, not proven by biopsy and did not require renal replacement therapy. Both patients, on regular supplementation with folic acid and vitamin B12, concomitantly developed myelosuppression and even several months after PEM withdrawal, showed only a modest improvement of renal function.
Conclusions: PEM is an antifolate antineoplastic agent with a broad-spectrum activity in locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC. It has been shown that PEM allows longer survival. The risk of acute or chronic kidney disease may be one of the prices to be paid for this success.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Nephrotoxicity; Pemetrexed.
References
-
- Santoro A, O’Brien ME, Stahe RA, Nackaerts K, Baas P, Karthaus M. et al. Pemetrexed plus cisplatin or pemetrexed plus carboplatin for chemonaive patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: results of the international expanded access program. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3(7):756–63. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31817c73d6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schuette WH, Groschel A, Sebastian M, Andreas S, Muller T, Schneller T. et al. A randomized phase II study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin as first-line therapy for patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2013;14(3):215–23. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2012.10.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Socinski MA, Stinchcombe TE, Hayes DN. The evolving role of pemetrexed (Alimta) in lung cancer. Semin Oncol. 2005;32(2 Suppl 2):16–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials