Non-junctional Cx32 mediates anti-apoptotic and pro-tumor effects via epidermal growth factor receptor in human cervical cancer cells
- PMID: 28492539
- PMCID: PMC5520707
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.183
Non-junctional Cx32 mediates anti-apoptotic and pro-tumor effects via epidermal growth factor receptor in human cervical cancer cells
Abstract
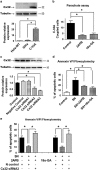
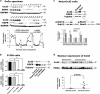
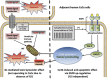
The role of connexin proteins (Cx), which form gap junctions (GJ), in progression and chemotherapeutic sensitivity of cervical cancer (CaCx), is unclear. Using cervix specimens (313 CaCx, 78 controls) and CaCx cell lines, we explored relationships among Cx expression, prognostic variables and mechanisms that may link them. In CaCx specimens, Cx32 was upregulated and cytoplasmically localized, and three other Cx downregulated, relative to controls. Cx32 expression correlated with advanced FIGO staging, differentiation and increased tumor size. In CaCx cell lines, Cx32 expression suppressed streptonigrin/cisplatin-induced apoptosis in the absence of functional GJ. In CaCx specimens and cell lines, expression of Cx32 upregulated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression. Inhibition of EGFR signaling abrogated the anti-apoptotic effect of Cx32 expression. In conclusion, upregulated Cx32 in CaCx cells produces anti-apoptotic, pro-tumorigenic effects in vivo and vitro. Abnormal Cx32 expression/localization in CaCx appears to be both a mechanism and biomarker of chemotherapeutic resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kumar NM, Gilula NB. The gap junction communication channel. Cell 1996; 84: 381–388. - PubMed
-
- Mehta PP, Bertram JS, Loewenstein WR. Growth inhibition of transformed cells correlates with their junctional communication with normal cells. Cell 1986; 44: 187–196. - PubMed
-
- Loewenstein WR KY. Intercellular communication and the control of tissue growth: lack of communication between cancer cells. Nature 1966; 209: 1248–1249. - PubMed
-
- Kanczuga-Koda LKM, Sulkowski S, Wincewicz A, Zalewski B, Sulkowska M. Gradual loss of functional gap junction within progression of colorectal cancer_ a shift from membranous CX32 and CX43 expression to cytoplasmic pattern during colorectal. In Vivo 2010; 24: 101–107. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

