Theoretical basis, application, reliability, and sample size estimates of a Meridian Energy Analysis Device for Traditional Chinese Medicine Research
- PMID: 28492726
- PMCID: PMC5401611
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2017(04)10
Theoretical basis, application, reliability, and sample size estimates of a Meridian Energy Analysis Device for Traditional Chinese Medicine Research
Abstract
Objectives:: The Meridian Energy Analysis Device is currently a popular tool in the scientific research of meridian electrophysiology. In this field, it is generally believed that measuring the electrical conductivity of meridians provides information about the balance of bioenergy or Qi-blood in the body.
Methods and results:: PubMed database based on some original articles from 1956 to 2014 and the authoŕs clinical experience. In this short communication, we provide clinical examples of Meridian Energy Analysis Device application, especially in the field of traditional Chinese medicine, discuss the reliability of the measurements, and put the values obtained into context by considering items of considerable variability and by estimating sample size.
Conclusion:: The Meridian Energy Analysis Device is making a valuable contribution to the diagnosis of Qi-blood dysfunction. It can be assessed from short-term and long-term meridian bioenergy recordings. It is one of the few methods that allow outpatient traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis, monitoring the progress, therapeutic effect and evaluation of patient prognosis. The holistic approaches underlying the practice of traditional Chinese medicine and new trends in modern medicine toward the use of objective instruments require in-depth knowledge of the mechanisms of meridian energy, and the Meridian Energy Analysis Device can feasibly be used for understanding and interpreting traditional Chinese medicine theory, especially in view of its expansion in Western countries.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures

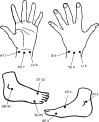
Similar articles
-
Different patterns of dynamic variations on electrical conductances of acupoints between Qi Vacuity and Qi non-Vacuity after glucose ingestion.J Altern Complement Med. 2011 Sep;17(9):843-9. doi: 10.1089/acm.2010.0528. Epub 2011 Aug 19. J Altern Complement Med. 2011. PMID: 21854198 Clinical Trial.
-
[Oxygen metabolism and meridian qi].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2012 Feb;32(2):183-6. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2012. PMID: 22493934 Chinese.
-
[Observation and analysis on the meridian-collateral running track-related anatomical structure in the human body].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2009 Jun;34(3):202-6. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2009. PMID: 19761118 Chinese.
-
Birdcage model for the Chinese meridian system: part VI. meridians as the primary regulatory system.Am J Chin Med. 2005;33(5):759-66. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X05003302. Am J Chin Med. 2005. PMID: 16265988 Review.
-
A "4D" systemic view on meridian essence: Substantial, functional, chronological and cultural attributes.J Integr Med. 2022 Mar;20(2):96-103. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2021.11.006. Epub 2021 Nov 27. J Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 34896049 Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Analysis of Microflora and Metabolites in the Development of Ulcerative Colitis into Colorectal Cancer Based on the Lung-Gut Correlation Theory.Molecules. 2022 Sep 8;27(18):5838. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185838. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144573 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapy in conjunction with traditional Chinese medicine for survival of patients with early female breast cancer: protocol for a non-randomized, single center prospective cohort study.Trials. 2019 Dec 17;20(1):741. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3848-8. Trials. 2019. PMID: 31847861 Free PMC article.
-
Cupping Therapy as an Adjunctive Therapy for Side Effects of Colorectal Cancer Treatment: A Prospective Observational Study.J Chiropr Med. 2022 Dec;21(4):280-287. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2022.02.011. Epub 2022 May 21. J Chiropr Med. 2022. PMID: 36420364 Free PMC article.
-
Meridian study on the response current affected by acupuncture needling direction.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 2;101(35):e30338. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030338. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36107585 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Physiological and Psychological Effects of Qigong Exercise in Older Practitioners.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Apr 2;2018:4960978. doi: 10.1155/2018/4960978. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 29805467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakatani Y. Skin electric resistance and ryodoraku. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1956;6:52.
-
- Tsai MY, Kuo CE, Huang YC, Hsieh CL, Chen YH, Chen WC. Meridian energy analysis of the immediate effect of coffee consumption. Eur J Integr Med. 2014;6((1)):74–81. doi: 10.1016/j.eujim.2013.09.002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

