Selumetinib Plus Docetaxel Compared With Docetaxel Alone and Progression-Free Survival in Patients With KRAS-Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The SELECT-1 Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 28492898
- PMCID: PMC5815037
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.3438
Selumetinib Plus Docetaxel Compared With Docetaxel Alone and Progression-Free Survival in Patients With KRAS-Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The SELECT-1 Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: There are no specifically approved targeted therapies for the most common genomically defined subset of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), KRAS-mutant lung cancer.
Objective: To compare efficacy of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitor selumetinib + docetaxel with docetaxel alone as a second-line therapy for advanced KRAS-mutant NSCLC.
Design, setting, and participants: Multinational, randomized clinical trial conducted at 202 sites across 25 countries from October 2013 through January 2016. Of 3323 patients with advanced NSCLC and disease progression following first-line anticancer therapy tested for a KRAS mutation, 866 were enrolled and 510 randomized. Primary reason for exclusion was ineligibility. The data cutoff date for analysis was June 7, 2016.
Interventions: Patients were randomized 1:1; 254 to receive selumetinib + docetaxel and 256 to receive placebo + docetaxel.
Main outcomes and measures: Primary end point was investigator assessed progression-free survival. Secondary end points included overall survival, objective response rate, duration of response, effects on disease-related symptoms, safety, and tolerability.
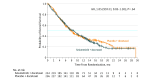
Results: Of 510 randomized patients (mean age, 61.4 years [SD, 8.3]; women, 207 [41%]), 505 patients (99%) received treatment and completed the study (251 received selumetinib + docetaxel; 254 received placebo + docetaxel). At the time of data cutoff, 447 patients (88%) had experienced a progression event and 346 deaths (68%) had occurred. Median progression-free survival was 3.9 months (interquartile range [IQR], 1.5-5.9) with selumetinib + docetaxel and 2.8 months (IQR, 1.4-5.5) with placebo + docetaxel (difference, 1.1 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.93 [95% CI, 0.77-1.12]; P = .44). Median overall survival was 8.7 months (IQR, 3.6-16.8) with selumetinib + docetaxel and 7.9 months (IQR, 3.8-20.1) with placebo + docetaxel (difference, 0.9 months; HR, 1.05 [95% CI, 0.85-1.30]; P = .64). Objective response rate was 20.1% with selumetinib + docetaxel and 13.7% with placebo + docetaxel (difference, 6.4%; odds ratio, 1.61 [95% CI, 1.00-2.62]; P = .05). Median duration of response was 2.9 months (IQR, 1.7-4.8; 95% CI, 2.7-4.1) with selumetinib + docetaxel and 4.5 months (IQR, 2.3-7.3; 95% CI, 2.8-5.6) with placebo + docetaxel. Adverse events of grade 3 or higher were more frequent with selumetinib + docetaxel (169 adverse events [67%] for selumetinib + docetaxel vs 115 adverse events [45%] for placebo + docetaxel; difference, 22%).
Conclusions and relevance: Among patients with previously treated advanced KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer, addition of selumetinib to docetaxel did not improve progression-free survival compared with docetaxel alone.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov: NCT01933932.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Treatment of KRAS-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The End of the Beginning for Targeted Therapies.JAMA. 2017 May 9;317(18):1835-1837. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.3436. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28492885 No abstract available.
-
Inhibition of MEK, a canonical KRAS pathway effector in KRAS mutant NSCLC.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2018 Sep;7(Suppl 3):S183-S186. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2018.03.20. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30393596 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Barlesi F, Mazieres J, Merlio JP, et al. ; Biomarkers France contributors . Routine molecular profiling of patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer: results of a 1-year nationwide programme of the French Cooperative Thoracic Intergroup (IFCT). Lancet. 2016;387(10026):1415-1426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

