MicroRNA-1 acts as a tumor suppressor microRNA by inhibiting angiogenesis-related growth factors in human gastric cancer
- PMID: 28493075
- PMCID: PMC5741792
- DOI: 10.1007/s10120-017-0721-x
MicroRNA-1 acts as a tumor suppressor microRNA by inhibiting angiogenesis-related growth factors in human gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: We recently reported that miR-1 was one of the most significantly downregulated microRNAs in gastric cancer (GC) patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas microRNA sequencing data. Here we aim to elucidate the role of miR-1 in gastric carcinogenesis.
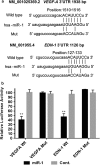
Methods: We measured miR-1 expression in human GC cell lines and 90 paired primary GC samples, and analyzed the association of its status with clinicopathological features. The effect of miR-1 on GC cells was evaluated by proliferation and migration assay. To identify the target genes of miR-1, bioinformatic analysis and protein array analysis were performed. Moreover, the regulation mechanism of miR-1 with regard to these predicted targets was investigated by quantitative PCR (qPCR), Western blot, ELISA, and endothelial cell tube formation. The putative binding site of miR-1 on target genes was assessed by a reporter assay.
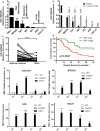
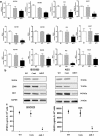
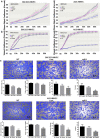
Results: Expression of miR-1 was obviously decreased in GC cell lines and primary tissues. Patients with low miR-1 expression had significantly shorter overall survival compared with those with high miR-1 expression (P = 0.0027). Overexpression of miR-1 in GC cells inhibited proliferation, migration, and tube formation of endothelial cells by suppressing expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) and endothelin 1 (EDN1). Conversely, inhibition of miR-1 with use of antago-miR-1 caused an increase in expression of VEGF-A and EDN1 in nonmalignant GC cells or low-malignancy GC cells.
Conclusions: MiR-1 acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting angiogenesis-related growth factors in human gastric cancer. Downregulated miR-1 not only promotes cellular proliferation and migration of GC cells, but may activates proangiogenesis signaling and stimulates the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells, indicating the possibility of new strategies for GC therapy.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Gastric cancer; Vascular endothelial growth factor A; miR-1.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals and informed consent
All samples were obtained with patients’ informed consent. The Ethics Committee of Beijing Cancer Hospital approved this study. This study does not involve animals.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray, F. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC CancerBase no. 11. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013. Available from http://globocan.iarc.fr - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

