A novel Filamentous Flower mutant suppresses brevipedicellus developmental defects and modulates glucosinolate and auxin levels
- PMID: 28493925
- PMCID: PMC5426679
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177045
A novel Filamentous Flower mutant suppresses brevipedicellus developmental defects and modulates glucosinolate and auxin levels
Abstract
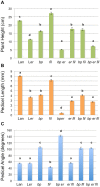
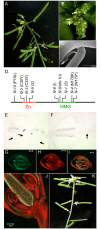
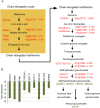
BREVIPEDICELLUS (BP) encodes a class-I KNOTTED1-like homeobox (KNOX) transcription factor that plays a critical role in conditioning a replication competent state in the apical meristem, and it also governs growth and cellular differentiation in internodes and pedicels. To search for factors that modify BP signaling, we conducted a suppressor screen on bp er (erecta) plants and identified a mutant that ameliorates many of the pleiotropic defects of the parent line. Map based cloning and complementation studies revealed that the defect lies in the FILAMENTOUS FLOWER (FIL) gene, a member of the YABBY family of transcriptional regulators that contribute to meristem organization and function, phyllotaxy, leaf and floral organ growth and polarity, and are also known to repress KNOX gene expression. Genetic and cytological analyses of the fil-10 suppressor line indicate that the role of FIL in promoting growth is independent of its previously characterized influences on meristem identity and lateral organ polarity, and likely occurs non-cell-autonomously from superior floral organs. Transcription profiling of inflorescences revealed that FIL downregulates numerous transcription factors which in turn may subordinately regulate inflorescence architecture. In addition, FIL, directly or indirectly, activates over a dozen genes involved in glucosinolate production in part by activating MYB28, a known activator of many aliphatic glucosinolate biosynthesis genes. In the bp er fil-10 suppressor mutant background, enhanced expression of CYP71A13, AMIDASE1 (AMI) and NITRILASE genes suggest that auxin levels can be modulated by shunting glucosinolate metabolites into the IAA biosynthetic pathway, and increased IAA levels in the bp er fil-10 suppressor accompany enhanced internode and pedicel elongation. We propose that FIL acts to oppose KNOX1 gene function through a complex regulatory network that involves changes in secondary metabolites and auxin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
flasher, a novel mutation in a glucosinolate modifying enzyme, conditions changes in plant architecture and hormone homeostasis.Plant J. 2020 Sep;103(6):1989-2006. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14878. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Plant J. 2020. PMID: 32529723
-
A novel allele of FILAMENTOUS FLOWER reveals new insights on the link between inflorescence and floral meristem organization and flower morphogenesis.BMC Plant Biol. 2010 Jun 28;10:131. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-131. BMC Plant Biol. 2010. PMID: 20584289 Free PMC article.
-
Pedicel development in Arabidopsis thaliana: contribution of vascular positioning and the role of the BREVIPEDICELLUS and ERECTA genes.Dev Biol. 2005 Aug 15;284(2):451-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.06.011. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 16038894
-
Auxin regulation of Arabidopsis flower development involves members of the AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE/PLETHORA (AIL/PLT) family.J Exp Bot. 2011 Jun;62(10):3311-9. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err127. Epub 2011 Apr 21. J Exp Bot. 2011. PMID: 21511900 Review.
-
Gynoecium and fruit development in Arabidopsis.Development. 2022 Mar 1;149(5):dev200120. doi: 10.1242/dev.200120. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Development. 2022. PMID: 35226096 Review.
Cited by
-
Association mapping of important agronomic traits in Mucuna pruriens (L.) DC.Bot Stud. 2024 Aug 19;65(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s40529-024-00421-3. Bot Stud. 2024. PMID: 39158798 Free PMC article.
-
The YABBY Family Transcription Factor AaYABBY5 Directly Targets Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase (CYP71AV1) and Double-Bond Reductase 2 (DBR2) Involved in Artemisinin Biosynthesis in Artemisia Annua.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Sep 10;10:1084. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01084. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31552076 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis in Artemisia annua by AaYABBY5.Hortic Res. 2021 Dec 1;8(1):257. doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00693-x. Hortic Res. 2021. PMID: 34848710 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Reveals Conserved Gene Expression in Reproductive Organs in Solanaceae.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 10;26(8):3568. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083568. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vollbrecht E, Reiser L, Hake S. Shoot meristem size is dependent on inbred background and presence of the maize homeobox gene, knotted1. Development. 2000;127:3161–3172. - PubMed
-
- Smith LG, Greene B, Veit B, Hake S. A dominant mutation in the maize homeobox gene, KNOTTED-1, causes its ectopic expression in leaf cells with altered fates. Development. 1992;116:21–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

