Direct estrogen receptor (ER) / HER family crosstalk mediating sensitivity to lumretuzumab and pertuzumab in ER+ breast cancer
- PMID: 28493933
- PMCID: PMC5426757
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177331
Direct estrogen receptor (ER) / HER family crosstalk mediating sensitivity to lumretuzumab and pertuzumab in ER+ breast cancer
Abstract
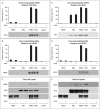
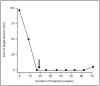
Bidirectional cross talk between members of the human epidermal growth factor family of receptors (HER) and the estrogen receptor (ER) is believed to underlie resistance mechanisms that develop in response to treatment with anti-HER agents and endocrine therapy. We investigated the interaction between HER2, HER3 and the ER in vitro using human embryonic kidney cells transfected with human HER2, HER3, and ERα. We also investigated the additive efficacy of combination regimens consisting of anti-HER3 (lumretuzumab), anti-HER2 (pertuzumab), and endocrine (fulvestrant) therapy in vivo. Our data show that both HER2 and HER3 can directly complex with the ER and can mediate phosphorylation of the ER. Phosphorylation of the ER was only observed in cells that expressed both HER2 and ERα or in heregulin-stimulated cells that expressed both HER3 and ERα. Using a mouse xenograft model of ER+/HER2-low (HER2 immunohistochemistry 1+ or 2+ without gene amplification) human breast cancer we show that the combination of lumretuzumab and pertuzumab is highly efficacious and induces long-lasting tumor regression in vivo and adding endocrine therapy (fulvestrant) to this combination further improved efficacy. In addition, a prolonged clinical response was observed with the combination of lumretuzumab and pertuzumab in a patient with ER+/HER2-low breast cancer who had failed endocrine therapy. These preclinical data confirm that direct cross talk exists between HER2/HER3 and ER which may explain the resistance mechanisms to endocrine therapy and monoclonal antibodies that target HER2 and HER3. Our data also indicate that the triplet of anti-HER2, anti-HER3, and endocrine therapy might be an efficacious combination for treating patients with ER+/HER2-low breast cancer, which is an area of significant unmet medical need.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phase Ib study evaluating safety and clinical activity of the anti-HER3 antibody lumretuzumab combined with the anti-HER2 antibody pertuzumab and paclitaxel in HER3-positive, HER2-low metastatic breast cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2018 Oct;36(5):848-859. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-0562-4. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Invest New Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29349598 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Different mechanisms for resistance to trastuzumab versus lapatinib in HER2-positive breast cancers--role of estrogen receptor and HER2 reactivation.Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):R121. doi: 10.1186/bcr3067. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22123186 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of the HER2/HER3 signaling axis overcomes ligand-mediated resistance to trastuzumab in HER2-positive breast cancer.Cancer Med. 2019 Mar;8(3):1258-1268. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1995. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 30701699 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic implications of estrogen receptor signaling in HER2-positive breast cancers.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Aug;135(1):39-48. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2067-8. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 22527112 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and clinical efficacy of pertuzumab in breast cancer therapy.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2015;11(10):1647-63. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2015.1078311. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26307328 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic correlations of HER3 expression and its degradation regulators, NEDD4-1 and NRDP1, in primary breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2018 Oct 26;18(1):1045. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4917-1. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30367623 Free PMC article.
-
HER3 receptor and its role in the therapeutic management of metastatic breast cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 17;22(1):665. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05445-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39020378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estradiol promotes rapid degradation of HER3 in ER-positive breast cancer cell line MCF-7.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018 Oct 26;16:103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2018.10.008. eCollection 2018 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2018. PMID: 30417127 Free PMC article.
-
HER3 signaling and targeted therapy in cancer.Oncol Rev. 2018 May 16;12(1):355. doi: 10.4081/oncol.2018.355. eCollection 2018 Jan 30. Oncol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30057690 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Estrogen Receptor Status on Circulatory Immune and Metabolomics Profiles of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Patients Enrolled for Neoadjuvant Targeted Chemotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jan 29;12(2):314. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020314. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32013102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987; 235: 177–82. - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y. Biology of HER2 and its importance in breast cancer. Oncology. 2001; 61 Suppl 2: 1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

